Design and Implementation of Multicast Video System Based on IP
This article focuses on the streaming media technology and its underlying transmission technology-IP multicast. Based on the campus network design and implementation of a video communication system for network live broadcast, video on demand and other services, the system combines the advantages of multicast technology to save bandwidth and reduce server load, and uses Real RealMedia streaming system, Completed in client / server mode.
1 Streaming media technology
The so-called streaming media refers to streaming media to play media files on the Internet, that is, after the entire audio, video and other continuous media files are compressed, the server continuously and real-time transmission to the user's computer. Users only need to go through a few seconds or tens of seconds to start the delay to play and watch, the rest will continue to download in the background, download while playing. There are two methods to realize streaming: Real-time streaming (Real TImes treaming) and sequential streaming (Progressive streaming). Among them, real-time streaming requires a dedicated streaming media server and transmission protocol (such as real-time transmission protocol RTP, real-time transmission control protocol RTCP, real-time streaming protocol RTSP, and media server protocol MMS, etc.) to ensure that the media signal bandwidth matches the network connection, so that the media It can be viewed in real time and is particularly suitable for live broadcast.
At present, the solutions that support streaming media technologies include RealNet works ’RealSystem, Microsoft ’s Windows MediaTechnology, and Apple ’s QuickTIme.
2 Multicast technology
From the perspective of the underlying transmission mode, real-time streaming supports unicast, broadcast, and multicast. The so-called multicast means that the data source sends the IP data packets "best effort" to a host group sharing the same IP address, and then uses the network device to perform the corresponding copy and distribution. Only members belonging to the group can receive the packet. data pack. Obviously, for online video live broadcast, because most users receive the same data, the use of multicast transmission mode is more than the point-to-point packet transmission method-unicast and one-point packet transmission method to all hosts-broadcast , Has obvious advantages in terms of saving network bandwidth, reducing server load, and easier implementation of distributed network applications.
Multicast uses Class D addresses in the IANAIP address classification, that is, the range is 224.0.0.0 ~ 239.255.255.255. On this basis, CERNET further divides the address space into four administrative domains: Internet range, CERNET backbone network, provincial network, and campus network. The multicast address space of the campus network is 239.251.192.0/18.
In addition, to achieve multicast at least: (1) Deploy the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) between the host and the router to manage the membership of the group. (2) Deploy a multicast routing protocol that forwards data packets between routers. Generally speaking, multicast routing protocols can be divided into two categories: one is dense mode, such as DVMRP, PIM-DM, MOSPF, etc., which is more suitable for environments with sufficient network bandwidth and dense distribution of group members; one is sparse mode, Such as PIM-SM, it is more suitable for the situation where the network bandwidth is limited and the group members are sparsely distributed. (3) In order to effectively suppress the proliferation of multicast packets at the link layer, IGMPSnooping needs to be deployed. It relies on IGMP messages listening to the communication between the host and the router to map the active members of the same multicast group to a VLAN. After receiving the multicast packet, it is only forwarded to the VLAN member corresponding to the multicast group.
3 System design and implementation
The system uses Real's RealSystem's streaming media system, combined with IP multicast technology, in the client / server mode, a streaming media communication system for online live broadcast, video on demand and other services is constructed as shown in Figure 1. Due to the slow start feature of TCP and the reliability guarantee of lost retransmission, it is not suitable for streaming media transmission, and even less suitable for multicast. Most of the current research is based on UDP MulTIcast, and RTP / RTCP is used as a framework for information feedback. Therefore, IP Multicast (IPMulTIcast) has become the best solution.
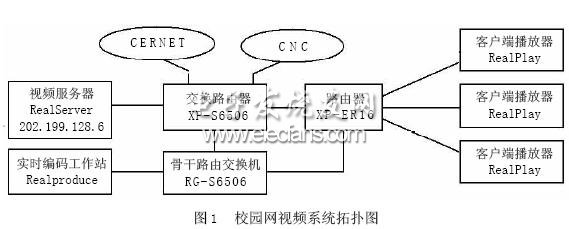
3.1 RealSystem streaming media system
3.1.1 Composition of RealSystem
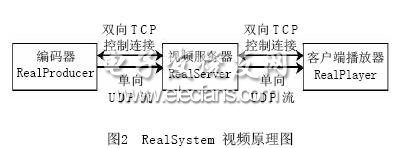
Real's RealSystem streaming media system is a system with excellent performance and very stable, and it has a high market share in the world. It uses a high-performance adaptive compression algorithm to generate a unique RM format file, can have a high compression ratio, and can adapt to the line requirements from 56kbit / s to more than 10Mbit / s bandwidth. Real's streaming media system is currently no one can replace in the real-time network live broadcast field, there are a large number of practical solutions to choose from, and it can adapt to the operating system of each platform. Currently available platforms include NT, Linux, Solaris, UNIX, AIX, and Irix systems. It is the system that currently supports the most platforms, and its working principle is shown in Figure 2.
Longkou Libo Insulating Material Co.,Ltd. , https://www.liboinsulation.com
