Classification, characteristics and closed-loop drive of AC servo motors
The rotor inside the servo motor is a permanent magnet. The U/V/W three-phase electric motor controlled by the driver forms an electromagnetic field. The rotor rotates under the action of the magnetic field. At the same time, the encoder feedback signal from the motor is supplied to the driver. The driver according to the feedback value and target. The values ​​are compared to adjust the angle at which the rotor rotates. The accuracy of the servo motor is determined by the accuracy (number of lines) of the encoder.
The structure of the AC servo motor can be mainly divided into two parts, a stator part and a rotor part. The structure of the stator is basically the same as that of the stator of the rotary transformer, and two-phase windings with a mutual electrical angle of 90 degrees are also placed in the stator core. One group is a field winding and the other is a control winding. The AC servo motor is a two-phase AC motor. When the AC servo motor is used, a constant excitation voltage Uf is applied across the excitation winding, and a control voltage Uk is applied across the control winding. When the stator winding is applied with a voltage, the servo motor will quickly turn. The current flowing into the field winding and the control winding generates a rotating magnetic field in the motor. The steering of the rotating magnetic field determines the steering of the motor. When the voltage applied to any one of the windings is reversed, the direction of the rotating magnetic field changes. The direction has also changed.

For a long time, in the occasions requiring high speed regulation performance, the governing system that has always dominated is the application of DC motor speed control system. However, DC motors have some inherent disadvantages, such as brushes and commutators that are prone to wear and require frequent maintenance. When the commutator is commutated, sparks are generated, the maximum speed of the motor is limited, and the application environment is limited. Moreover, the structure of the DC motor is complicated, manufacturing is difficult, the steel material used is expensive, and the manufacturing cost is high. AC motors, especially squirrel cage induction motors, do not have the above disadvantages, and the rotor inertia is smaller than that of DC motors, resulting in better dynamic response. In the same volume, the output power of the AC motor can be increased by 10% to 70% compared with the DC motor. In addition, the capacity of the AC motor can be made larger than that of the DC motor to achieve higher voltage and speed. Modern CNC machine tools tend to use AC servo drives, and AC servo drives have replaced the trend of DC servo drives.
Asynchronous
The asynchronous AC servo motor refers to an AC induction motor. It has three-phase and single-phase, squirrel-cage and wire-wound, and usually uses a squirrel-cage three-phase induction motor. The structure is simple, compared with the same capacity DC motor, the quality is 1/2 light, and the price is only 1/3 of the DC motor. The disadvantage is that it is not economically possible to achieve a wide range of smooth speed regulation, and it is necessary to absorb the lagging excitation current from the grid. As a result, the power factor of the grid is deteriorated.
The asynchronous AC servo motor of the squirrel-cage rotor is simply referred to as an asynchronous AC servo motor and is represented by IM.
Synchronous type
Although the synchronous AC servo motor is more complicated than the induction motor, it is simpler than the DC motor. Its stator, like the induction motor, is equipped with a symmetrical three-phase winding on the stator. The rotors are different. According to different rotor structures, they are divided into two types: electromagnetic and non-electromagnetic. Non-electromagnetic is divided into magnetic hysteresis, permanent magnet and reactive. Among them, the hysteresis type and the reactive synchronous motor have the disadvantages of low efficiency, poor power factor, and small manufacturing capacity. Permanent magnet synchronous motors are often used in CNC machine tools. Compared with the electromagnetic type, the permanent magnet has the advantages of simple structure, reliable operation and high efficiency; the disadvantage is that the volume is large and the starting characteristics are not good. However, the permanent magnet synchronous motor adopts high residual magnetization and high coercivity rare earth magnets, which can be about 1/2 smaller than the DC electric shape, 60% lighter, and the rotor inertia is reduced to 1/5 of the DC motor. Compared with asynchronous motors, it uses high-magnet excitation to eliminate excitation loss and related stray losses, so it is efficient. Moreover, because there is no collector ring and brush required for the electromagnetic synchronous motor, the mechanical reliability is the same as that of the induction (asynchronous) motor, and the power factor is much higher than that of the asynchronous motor, so that the volume ratio of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is asynchronous. The motor is smaller. This is because at low speeds, the induction (asynchronous) motor has a much higher apparent power than the apparent power, because the power factor is low and the output of the same active power is much larger.
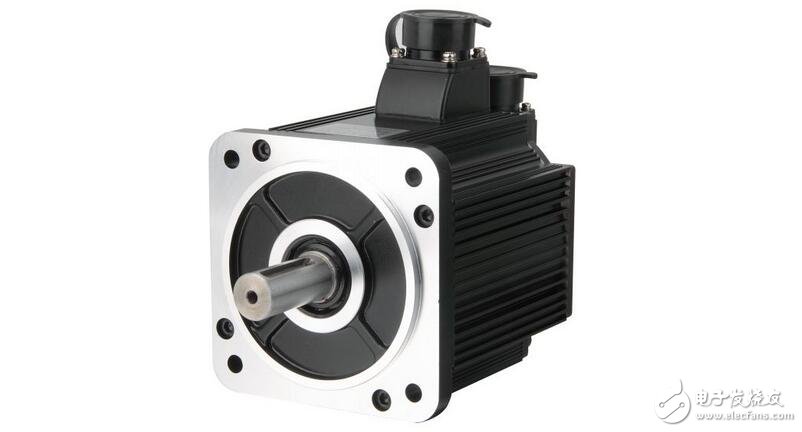

The AC motors used on CNC machines are generally three-phase. Divided into: asynchronous and synchronous AC servo motors.
Synchronous AC motors are classified into two types: electromagnetic and non-electromagnetic, from the source of the magnetic potential that establishes the required air gap magnetic field. Non-electromagnetic type has a variety of hysteresis, permanent magnet and reactive. Hysteresis and reactive synchronous motors have the disadvantages of low efficiency, poor power factor, and small manufacturing capacity.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor:


Therefore, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is often used in the CNC machine feed drive system.
Asynchronous AC servo motor:
Compared with DC motors of the same capacity

Therefore, an asynchronous AC servo motor is used in the spindle drive system.
The difference between synchronous and asynchronous:
(1) AC synchronous motor: The rotor is made of permanent magnet material. After the rotation, as the rotating magnetic field of the stator changes, the rotor also changes the speed of the corresponding frequency, and the rotor speed is equal to the stator speed, so it is called “synchronousâ€.
(2) AC asynchronous motor: The rotor is composed of an induction coil and a core material. After the rotation, the stator generates a rotating magnetic field, the magnetic field cuts the induction coil of the rotor, the rotor coil generates an induced current, and the rotor generates an induced magnetic field, and the induced magnetic field follows the change of the rotating magnetic field of the stator, but the magnetic field change of the rotor is always smaller than the change of the stator magnetic field. The key parameter slip ratio in an AC asynchronous motor represents the ratio of the rotor to stator speed difference.
1. Permanent magnet AC synchronous motor
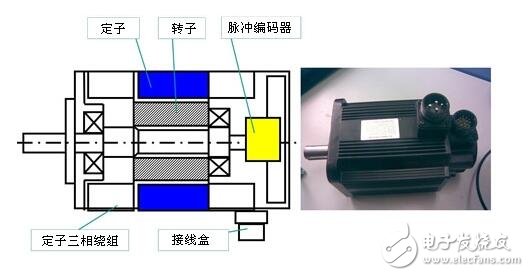
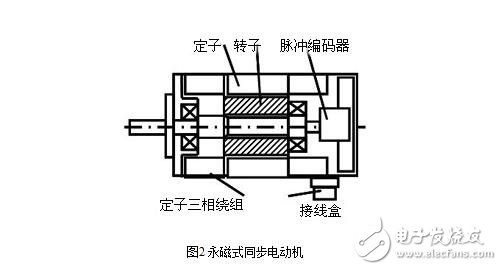
Structure: The motor consists of a stator, a rotor and a sensing element.
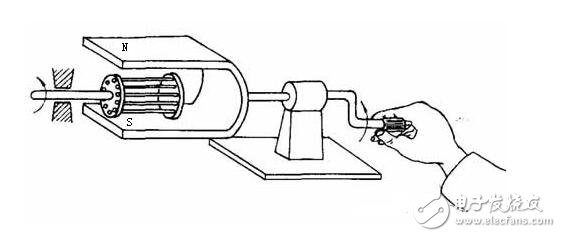
Two revelations:
First, there is a rotating magnetic field;
Second, the rotor rotates with the magnetic field.
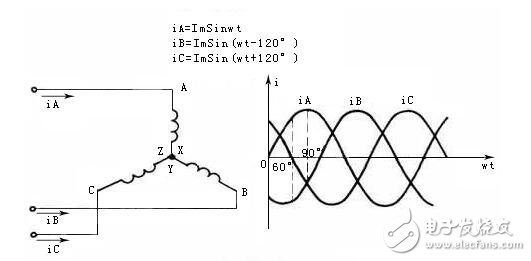
Three-phase symmetrical current
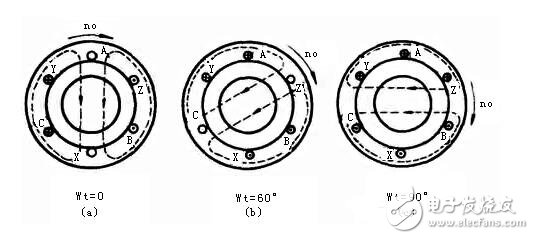
Rotating magnetic field generated by three-phase current (p=1)
Permanent magnet AC synchronous motor working principle and performance

Where nr is the rotational speed of the rotor; ns is the synchronous rotational speed; θ is the angle between the axis of the rotor pole and the axis of the stator pole; f1 is the AC power frequency (stator supply frequency); p is the pole pair of the stator and the rotor.
2, AC spindle motor
The three-phase winding of the stator is connected to the three-phase alternating current to generate a rotating magnetic field. The magnetic field cuts the conductor in the rotor, and the induced current of the conductor interacts with the magnetic field of the stator to generate electromagnetic torque, which drives the rotor to rotate, and the rotational speed nr is
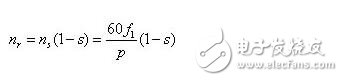
Where ns is the synchronous speed; f1 is the AC power frequency (stator power supply frequency); s is the slip rate, s = (ns-nr) / ns;
p is the pole logarithm.
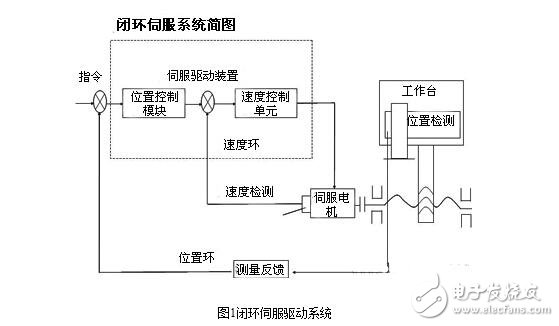
Closed-loop drive of AC servo motorThe closed-loop control system is a position servo system that directly measures and controls the displacement of the CNC machine table using a linear position detecting device (linear induction synchronizer, long grating, etc.). The control principle is shown in Figure 1. This system has a position detection feedback circuit and sometimes a speed feedback circuit.
1. Types of AC synchronous servo motors
Excitation, permanent magnet, magnetoresistive and hysteresis
2. Structure of permanent magnet AC synchronous servo motor
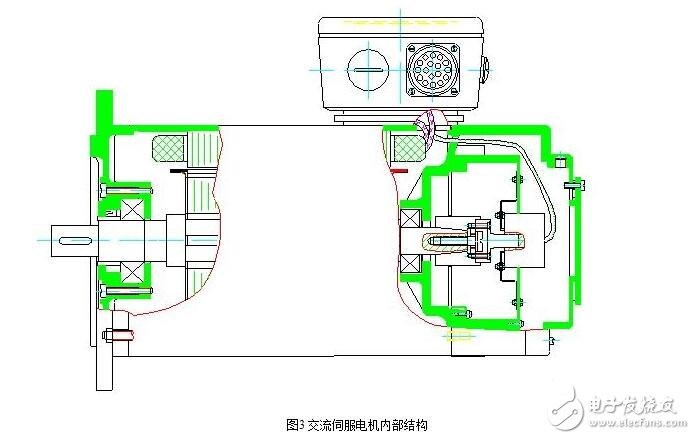
The motor consists of a stator, a rotor and a sensing element. See Figure 2. Its internal structure is shown in Figure 3.
3. Working principle and performance of permanent magnet AC synchronous servo motor
When the three-phase stator winding is connected to the three-phase alternating current, a synchronous rotating magnetic field is generated between the stator and the rotor, and the rotor is a permanent magnet, and under the action of the magnetic force, the rotor rotates synchronously following the rotating magnetic field.
As long as the load does not exceed a certain limit, there will be no AC synchronous motor out-of-step phenomenon. The maximum limit of this load is called the maximum synchronous torque.
Solve the problem that the synchronous motor is difficult to start by reducing the rotor inertia or increasing the speed of the motor to the required speed.
Main parameters: rated power, rated torque, rated speed, etc.
Advantages of AC servo motor:
â—† Dynamic response is good;
â—† Large output power, voltage and speed increase.
4. Speed ​​regulation method of permanent magnet AC synchronous servo motor
The feed system often uses an AC synchronous motor. The motor has no slip and the motor speed is
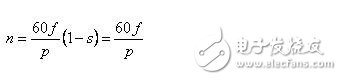
Speed ​​control method: frequency control
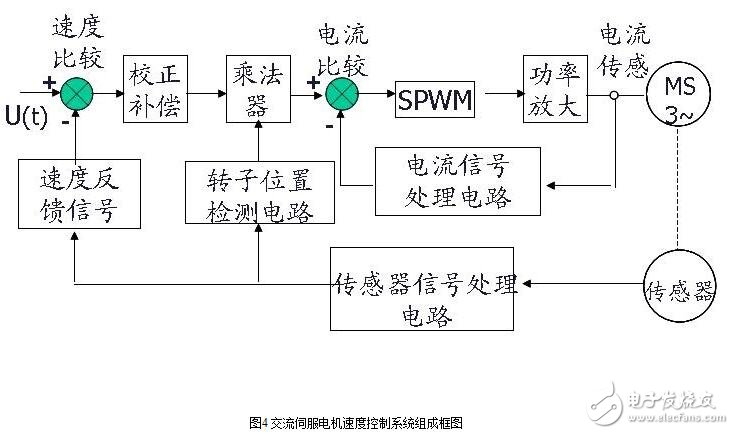
5. AC feed servo motor speed control system
System components: speed loop, current loop, SPWN circuit, power amplifier circuit, detection feedback circuit. See Figure 4.
Stylus Pen Tip,Stylus Pencil Tip,Carbon Fiber Pen Tip,Carbon Fiber Stylus Pen Tip
Shenzhen Ruidian Technology CO., Ltd , https://www.wisonen.com
