Focus on carbon nanodot carbon nanoparticle technology or change the future lighting market
A few days ago, the research team of Qu Songnan, a researcher at the Changchun Institute of Optoelectronics, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, broke through the problem of low luminous efficiency of carbon nanodots in the near-infrared band. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging.
In recent years, Qu Songnan led the research group to frequently publish articles in journals with high impact factors. Qu Songnan, who participated in the work in 2009, led the research group independently after several years of work, and was therefore promoted to a researcher.
Focus on carbon nanodotsQu Songnan pointed out that luminescent carbon nano-dots are emerging nano-luminescent materials, which have the advantages of small size (less than 20 nanometers), non-toxic, good luminous performance, good biocompatibility, good light stability, wide range of raw materials, and easy modification. , Causing widespread concern at home and abroad.
Earlier, the research on luminescent inorganic semiconductor nanoparticles was very active, but inorganic semiconductor nanoparticles generally contain heavy metal cores (lead and cadmium), which are toxic and harmful to the environment, so scientists began to prepare new non-toxic compounds Glowing nanoparticles.
In 2006, scientists at the Clemson University in the United States created a carbon nanoparticle that emits bright light under light. Scientists have also found that luminescent carbon nanoparticles have unique advantages, such as chemical stability, matte flicker, light bleach resistance, non-toxicity, relatively low cost, and excellent biocompatibility.
In 2012, the team of Qu Songnan, who was then an associate researcher at the Changchun Institute of Optoelectronics, discovered that the use of carbon nanoparticles to excite wavelength-dependent characteristics, combined with organic dyes, can construct graphics with information encryption on biological products, which can be applied to Information storage and information encryption.
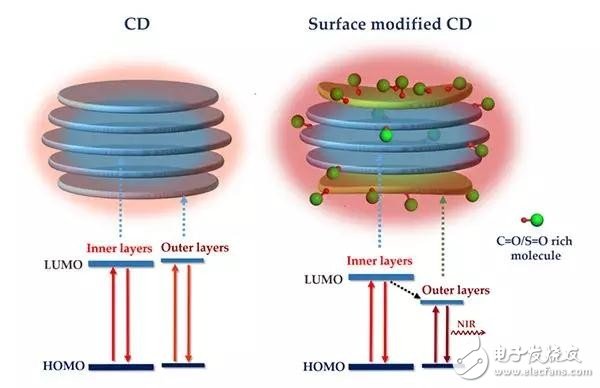
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the construction of near-infrared absorption / emission carbon nanodots and their luminescence mechanism after modification with surface electron-withdrawing groups.
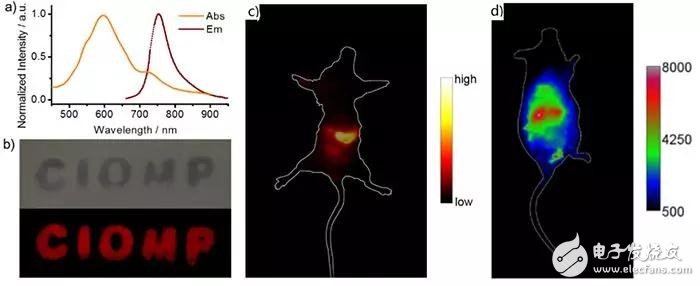
Figure 2. (a) Absorption and emission spectra of carbon nanodot @PVP complex. (bd) Near-infrared fluorescence imaging with carbon nanodots @ PVP complex as imaging reagent (b) and live-near-infrared fluorescence imaging of blood circulation in mice stomach (c) and tail vein injection (d).
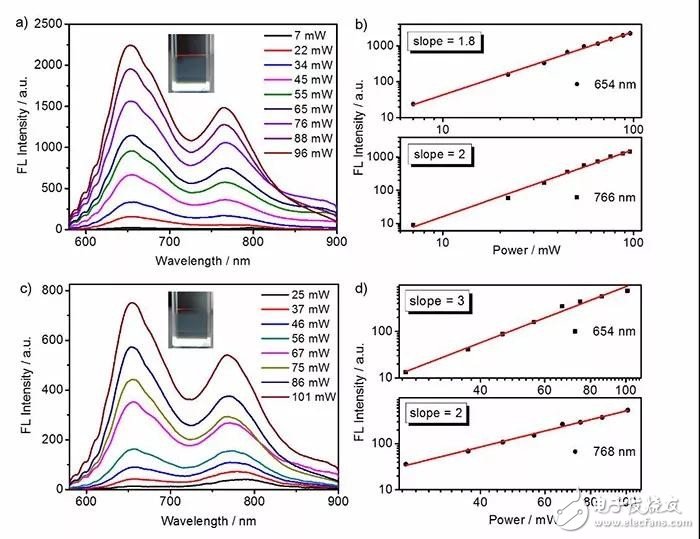
Figure 3. Femtosecond light in the near infrared-II region stimulates multi-photon-induced luminescence of carbon nanodots. (ab) The emission spectrum and luminous intensity-excitation light power curve of carbon nanodots excited by 1200 nm femtosecond light, (cd) The emission spectrum and luminous intensity-excitation light power curve of carbon nanodots excited by 1400 nm femtosecond light.
"These unique properties make it possible for carbon nanodots to enter our real life." Qu Songnan told reporters, and then their team developed a new type of fluorescent ink. "This ink can be applied to many fields such as bio-imaging, bio-product identification, information storage, information encryption, anti-counterfeiting, lighting display, sensing, photovoltaic devices, etc."
Break through the technical bottleneckIt is reported that the research on the luminescence mechanism of carbon nanoparticles and the spectrum regulation are the difficulties in this field. Before 2013, it was believed that the emission of carbon nanoparticles in the green light band originated from the surface defects of carbon nanoparticles, and this source of luminescence was considered to be difficult to achieve laser light.
To this end, Qu Songnan ’s team realized the regulation of the blue and green light emitted by the carbon nanoparticles by regulating the nitrogen element in the carbon nanoparticles. The phenomenon of amplified spontaneous emission of carbon nanoparticles in the green light band was observed, and was achieved for the first time. Optically pumped laser with carbon nanoparticles in the green band.
Qu Songnan recalled: "At that time, we proved by comparison experiments that the light stability of carbon nanoparticles is better than traditional organic laser dyes, indicating that carbon nanoparticles can be used as a new type of low cost, green environmental protection, and good light stability. Laser materials are expected to change the future lighting world. "
Subsequently, Qu Songnan and his research team first proposed the concept of "super carbon nanodots" internationally, and developed a water-based "nano fluorescent bomb" based on "supercarbon nanodots", making carbon nanodot materials a kind of New type of intelligent luminescent material.
The existing absorption and emission bands of carbon nano-dots are mainly located in the ultraviolet-visible region, and they cannot achieve efficient absorption in the near-infrared region and high fluorescence quantum efficiency near-infrared luminescence, which seriously limits the carbon nano-dots in biological fluorescence imaging, especially Application of in vivo near infrared fluorescence imaging.
In recent years, in response to the problem of achieving efficient near-infrared luminescence, Qu Songnan ’s group has modified the surface of red carbon nanodots by electron-withdrawing groups and disordered control of the ordered structure of the carbon-based inner core layer. A new luminescence band gap is generated in the wave band, and carbon nano-dots with high-efficiency near-infrared emission under near-infrared light excitation are obtained. The fluorescence quantum efficiency reaches 10%, which is the highest international value.
Post high-level articlesIt is not difficult to find that Qu Songnan's research group has carried out a lot of research in the field of luminescent carbon nano-dot energy band regulation and application. As the first author or corresponding author, Qu Songnan has published a total of 29 SCI papers, including 6 papers with an SCI impact factor of 10 or more. The first author paper has a maximum of 390 citations in a single SCI and a total of 1630 SCI citations. Among them, two articles published by Qu Songnan were selected as ESI (Basic Scientific Indicators Database) hot and highly cited papers, and were among the best one-thousandth papers.
Talking about how to publish high-level papers, Qu Songnan humbly stated that there is not much skill in this area. The first is that the research direction must be valuable and promising, and the second is that the research content must be the core problem in the field and the current The main challenge. "The two points are satisfied, and the quality of the published articles will not be bad."
Currently, Qu Songnan's scientific research plan is to make carbon nanodots reach clinical application in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment within 10 years.
He said: "Compared with the existing nano-luminescent materials, luminescent carbon nano-dots are particularly suitable for the development of biological imaging and cancer diagnosis and treatment drugs. In addition, the carbon nano-point fluorescence lifetime is only a few nanoseconds, much lower than the existing Commercial phosphors have important application potential in the field of high-bandwidth visible light lighting communications. "
As a young scientific researcher, Qu Songnan suggested that young people engage in scientific research first by looking at the scientific research conditions and development potential. "The state's guidance to scientific research personnel and various mechanisms and measures are getting better and better. As long as young people are willing to work in the right direction, they will get support." He also hopes that the country will have more tilts towards the northeast in terms of talent policy, and Young scientific researchers give more policy support in the transformation of results.
Ac Controller,Gigabit Wlan Controller,Enterprise Ac Gateway,Wireless Ap Controller
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com
