Intel White Paper: UWB Technology Enables High-Speed ​​Wireless Personal Area Network
The wireless connection injects convenience into the user's new mobile lifestyle. Consumers will soon have a huge demand for the convenience of this electronic home, their personal computers, digital video recorders, MP3 players, digital camcorders, digital cameras, high definition television (HDTV), set-top boxes (STB), games Systems, PDAs, mobile phones, etc. can be connected to each other via a wireless home personal area network (WPAN). However, today's WLAN and wireless personal area network technologies cannot meet the high bandwidth requirements of a large number of consumer electronic devices in the future. This requires new technologies to meet the needs of high-speed WPANS.
Ultra-Bandwidth (UWB) technology provides a solution for the bandwidth, cost, power, and physical needs of next-generation consumer electronics devices. This new technology provides high bandwidth to make multi-function digital cameras and stereos a reality throughout the home. With the support of industry groups, such as the USB Association, technology leaders, such as INTEL, UWB technology will strive to make home life high-speed WPANS connection easy and become a reality.
Introduction:
The mobile lifestyle brought about by the wireless technology of mobile phones and home PCs has led to an increasing demand for wireless devices for other devices. Consumers are enjoying the convenience of wireless connectivity. The technologies used in many digital homes, such as digital video and audio streams, require high bandwidth connections. Other wireless networking technologies developed for PCs wireless connectivity, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, are not sufficiently optimized compared to high-bandwidth usage models. Although Wi-Fi's data transfer rate can reach 54Mbps, this technology has limitations in the consumer electronics environment, including energy consumption and bandwidth. When connecting to consumer electronics devices in short-range networks or WPANs, wireless technologies need to support high data streams, low power consumption, low cost, and are suitable for ultra-small packages such as PDAs or mobile phones. Silicon development for the new UWB wireless technology and UWB applications will provide the best solution.
This document describes the use of UWB technology and potential UWB technology applications in digital home WPANs.
UWB case:
The new digital home environment is made up of many different consumer electronics, mobile devices, and personal computer devices that support diverse applications. These devices can be grouped into three broad categories (Table 1):
-PC and network
- Consumer electronics and wireless playback systems
- mobile and handheld devices
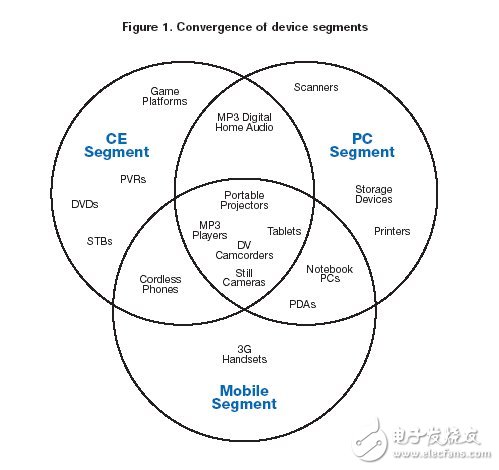
Next-generation PCs, consumer electronics and mobile applications are placing higher demands on connection speeds, far more than 1 Mbps of Bluetooth technology, which is used today in many WPANs. However, many consumer electronic devices cannot support the cost and power consumption required for high-speed 802.11a/b/g over Wi-Fi networks.
Although Wi-Fi technology is much faster than Bluetooth, it still cannot efficiently transmit multi-threaded concurrent high-quality video streams. UWB technology can provide the input and output required by next-generation integrated devices. With the support of WiMedia Alliance, it can ensure interactivity between various protocols such as IEEE 1394, USB, and UPnP, making UWB a high-speed, low-cost, A broad solution for low energy WPANs.
UWB technology:
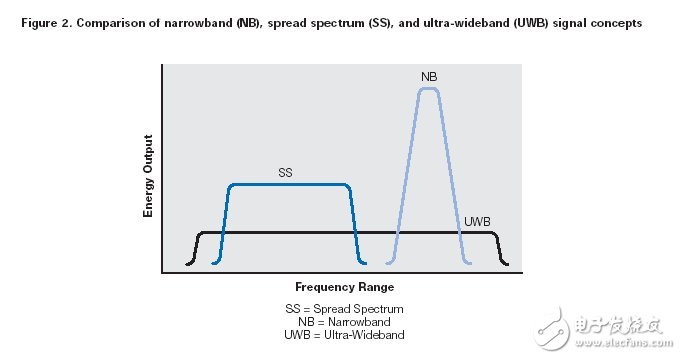
UWB is very different from other traditional narrowband radio frequency (RF) and spread spectrum technologies (SS) such as Bluetooth and 802.11a/b/g. UWB uses the ultra-wide bandwidth of the RF spectrum to pass data (Figure 2). UWB can deliver more data in a certain amount of time than traditional technology.
The potential data transfer rate on the RF link is proportional to the channel bandwidth and signal-to-noise ratio function (Shannon's Law). RF design engineers have no control over bandwidth parameters because this is dictated by the FCC. Bluetooth technology, 802.11a/b/g Wi-Fi, cordless phones and many other devices are classified as unlicensed, providing 900MHz, 2.4GHz, 5.1GHz. Each channel is limited to occupy only a very narrow band.
The spectrum of UWB has recently been legalized. UWB can use frequencies from 3.1 GHz to 10.6 GHz. Each channel can have a bandwidth of more than 500 MHz, depending on its center frequency. The FCC imposes strict wireless energy constraints on the distribution of such large broadband. In this way, the energy released by UWB devices when using large frequency bandwidths is not perceived by other narrow bandwidths nearby, such as 802.11a/b/g. This spectrum sharing allows the device to achieve very large input and output, but the distance must be very close.
The low energy consumption of UWB also makes it possible to develop UWB cost-saving CMOS. With limited power consumption, low cost, and high data transfer rate, UWB has begun to formally enter the high-speed WPAN market with these features.
UWB technology also allows for spectrum reuse. A close-up combination of devices (such as a home entertainment system) can communicate with another device in another room (such as a bedroom gaming system) on the same channel. The range of UWB-based WPANS is very short, and devices in the same channel nearby do not interfere with each other. However, the 802.11g WLAN solution quickly runs out of data bandwidth in a single device combination so that the sound channels in the home cannot be reused. Because of the limited scope of UWB technology, the 802.11 WLAN solution is the best complement to WPAN and can serve as a hub for data transmission between home computing devices.
UWB application:
UWB technology is suitable for a variety of WPAN applications. include:
- Replace the cable with a wireless connection between portable multimedia consumer electronics such as camcorders and digital cameras and MP3 players.
- Enable high-speed wireless USB connection between PC and PC external, including printers, scanners and external storage devices.
- Replace the next-generation Bluetooth technology devices such as 3G mobile phones, wired connections based on IP/UPnP and next-generation IP PC/CE/mobile devices.
- Establish an ad-hoc (point-to-point) high bit rate wireless connection between CE, PC and mobile device.
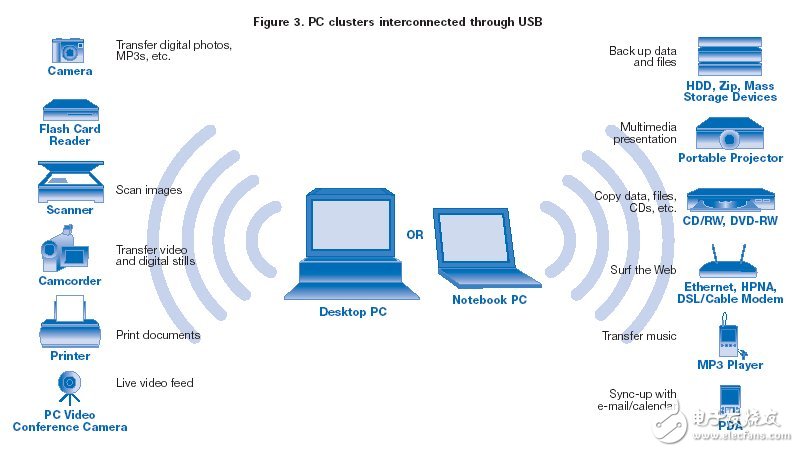
Wireless PC external device connection:
Today's wired USB has a certain market share, and the PC platform is connected to each other as shown in (Figure 3). But the wiring connection is not very convenient, and the Bluetooth technology only solves the problem to a certain extent, and there are still limitations. Wireless USB with UWB technology will provide solutions for users who want to use wireless USB. UWB will be able to take a large share of the PC external device connection market. The Wireless USB Working Group will set the standard for this by providing a speed of over 480Mbps (equivalent to wired USB 2.0) within 10 meters.
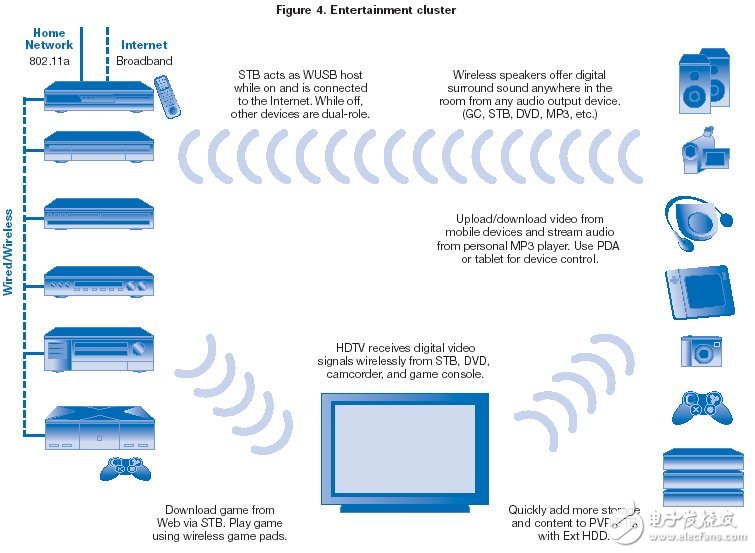
Wireless multimedia connection of CE equipment:
The wireless multimedia connection of the CE device for sound and image is closely related to the PC external device. As with the benefits of PCs and external devices, wireless convenience and data transfer capabilities are major advantages. The variety of entertainment combination devices is very broad, as shown in (Figure 4): DVD, HDTV, STB, PVR, MP3, surround sound, digital camcorders and digital cameras and other CE devices. For example, UWB can connect STB or DVD to a wall-mounted plasma TV or HDTV without affecting the aesthetic wires.
UWB can also connect PCs to entertainment devices, such as digital camcorders connected to a PC for digital image editing or large LCD playback. Connect your digital camera to your laptop for editing and send pictures by e-mail. See the key advantages of UWB (Listing 1). WPANS with UWB technology, once the devices are close enough to recognize each other, the user can simply tap the send button to transfer data.
Listing 1: Features and benefits of UWB in entertainment and PC environments

Wire replacement and network for mobile computer devices:
Complex wires are extremely inconvenient for users of mobile devices. Many devices, such as personal handhelds, are connected via a USB port, but other devices like 3G phones require special connectors. UWB devices can be connected to each other without wires when they are close enough. UWB has fast transmission speed and low energy consumption in hot spots.
The coverage of the hotspot network enables mobile computer devices to access the network broadband, creating a huge market. Today, there are only two technologies that support hotspots: 802.11a/b/g WLAN and Bluetooth-based WPAN. But both technologies are limited, and UWB will overcome these difficulties.
Ad-hoc (point-to-point) connection between UWB devices:
Like Bluetooth, each UWB device can act as a content source and receiver. It is possible to apply and connect a digital camera directly to the printer to print pictures.
Technical considerations:
In order to make UWB technology a widely adopted wireless solution, the following points need to be resolved:
- mutual operability
- Convenient product integration and certification
- Total solution cost (OEM)
- Global spectrum allocation
Intel is addressing these issues through investment strategies, research, participation in wired and wireless communications, and product development. Intel is also taking advantage of the advantages of UWB technology to develop protocols. The work done by the Wireless USB Working Group and the Digital Home Working Group to feed the WUSB standard is an example of Intel learning.
The Future: Wireless Free Intel
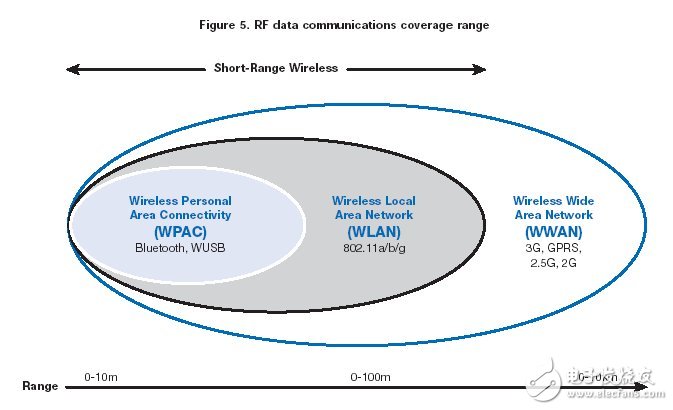
Intel is committed to wireless technology. The company has a vision for the ingenious wireless connectivity of all future devices. This vision is called wireless free Intel, giving the concept of sophisticated wireless, revisiting spectrum and applications. Configure WLAN hotspots with 802.11 wireless, Bluetooth technology, UWB wireless WPAN. To achieve these visions, Intel is working in all areas of RF space (Figure 5). In Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN), Intel supports WiMAX. In the WLAN space, Intel continues to promote Centrino mobile technology. Now, with UWB technology support for WPAN, the concept of Intel wireless freedom is only one step away from implementation.
to sum up:
UWB and related network protocols are in the early stages of development, and key deployment steps are being defined and evaluated. UWB complements the wireless networks deployed in today's WLAN environments, extending high bit rates, multimedia connectivity to WPANS, and support for PC, CE and mobile devices. This combination will enable the convergence of computers, consumer electronics and mobile communications.
The common wireless platform seamlessly integrates with existing network protocols, effectively reducing costs, and CE external solutions will change the environment for home entertainment.
Many UWB components and systems are already in the testing and demonstration phase, and the date of actual consumer product release is expected to be in early 2005. Intel is working with the industry to ensure the success of this technology.
Stainless Steel Shaped Tube,Disposable SS Shaped Tube For Laboratory,Medical Stainless Steel Shaped Tube,High Precision Stainless Steel Shaped Tube
ShenZhen Haofa Metal Precision Parts Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.haofametals.com
