Structure and construction of machine vision system
The composition of the machine vision system
General machine vision systems mainly include information detection, acquisition systems, image processing, display and intelligent decision-making modules, including computer graphics, digital image processing, video information processing, pattern recognition, artificial intelligence theory, intelligent information processing, VLSI technology and other technologies. It can be widely used in many fields such as automatic detection of industrial products, aerospace, aviation, remote sensing, satellite reconnaissance, astronomical observation, communication, transportation, electronics, finance, medical and other image acquisition, processing and decision-making. Figure 1 is a block diagram of a machine vision system.
Embedded image acquisition and processing system
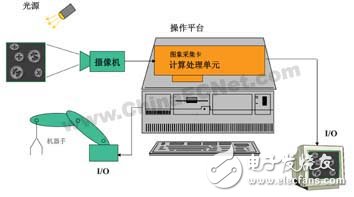
NetSighTII is a fully-featured embedded image acquisition and processing system that can quickly and easily form a machine vision system on the production line, solving the machine vision system consisting of PC/image capture card or smart camera in the actual production environment. Various problems have improved the quality of product production. The NetSighTII system is shown in Figure 2.
---NetSighTII embeds a high-performance processor, multiple camera interfaces, flexible communication device interfaces, and multiple user interfaces. Simply connect the camera to the NetSighTII and install the appropriate software to test the product on the production line, saving a lot of installation and debugging time.
--- SmartCamera can't detect multi-angle objects. If these cameras are matched with each other, the complexity and reliability of the system becomes a problem. The cost-effective NetSight II system can simultaneously view and process images of four cameras, and can also select the corresponding camera according to specific application requirements. NetSight II supports most standard, high-resolution (megapixel) analog cameras that can be connected to non-standard cameras via adapters.
--- NetSight II's machine vision inspection software Sherlock is a powerful automated inspection tool. There are thousands of inspection devices in the world using Sherlock software. Sherlock software is easy to use, well-configured, can quickly form templates, reference standards, etc., supports user-defined algorithms and user interfaces, but does not currently support color camera input.
Main characteristics and technical parameters

NetSight II system can automatically detect irregular devices online, process multiple video images at the same time, support multiple cameras, and powerful embedded processor to ensure fast detection and provide users with ideal machine vision system solutions.
The data acquisition part includes 3 monochrome or 1 RGB analog cameras, 15-pin D-Sub connectors, supports standard 640×480, 1024×1024 or higher resolution formats, and can simultaneously acquire 3 monochrome syncs. Camera or 1 color camera image. The memory is 256MB of program memory and 20GB of data memory. The digital input section supports 7 general-purpose codes for control switching and supports 30V TTL circuits. The digital output section includes seven interfaces for detection and control for optical gating.
External interface
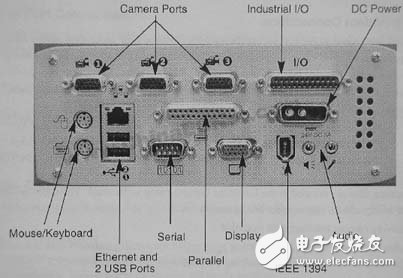
The operation interface includes standard VGA display, standard PS/2 mouse and keyboard or USB mouse and keyboard, USB interface for connecting additional USB compatible devices; network interface is 10/100Base-T Ethernet interface; camera (video) interface includes 3 Synchronous camera input (supports sequential scanning of standard or two-speed analog cameras, each camera's maximum image resolution is 2K x 2K pixels), 1 RGB camera input (supports sequential scanning of standard or two-speed analog cameras, maximum image size) It is 1K×1K), it can't support RGB and 3 simultaneous camera inputs at the same time; 1 IEEE1394 interface; 3 15-pin D-Sub interfaces on the back panel (marking video 1, 2, 3), video 1 interface supports monochrome And RGB cameras, Video 2 and Video 3 only support monochrome cameras, all interfaces can not support both monochrome and color cameras, but can simultaneously capture and process data from 3 monochrome cameras; provide 1 RS-232/485 compatible Serial port, when disconnected from the network, the port can control the main application; a standard parallel port can be used to connect parallel devices such as printers; AC97 compatible audio interface is used to issue audio alarm notifications. The back panel of NetSight II is shown in Figure 3.
Camera selection
Machine vision systems require the camera to capture images. The type of camera selected can indicate the system's ability to recognize, which means that the smallest information that can be identified is a function of the field of view. In other words, the camera can expand the field of view by changing the lens, but reduces the actual recognition area. Many factors, such as the source, lens distortion, and the position of the object, affect the quality of the image. It is common practice to fill the image of the image of interest on the sensor as much as possible while allowing registration errors and positional repetition. For example, if you need to detect a capillary crack in a large picture, you need a camera with a resolution that can identify the crack. In general, a standard or megapixel resolution camera can be used to solve machine vision applications.
Different types and manufacturers of machine vision cameras have their own unique characteristics, most of the cameras in the current production environment are analog monochrome cameras (that is, only the brightness and grayscale of the image can be detected). In addition to "static" operations (detected images cannot be moved), most cameras can now scan progressively so that the camera can accurately capture moving images and use them in special production environments. It should be noted that the light source and lens will have a large impact on camera performance.
Machine vision development software
Sherlock is a Windows-based machine vision development software that is easy to use and is ideal for developing machine vision applications. Sherlock has two economical and practical versions of SherlockEssential and SherlockProfessional, which can meet the different needs of enterprises. SherlockEssential is the most "basic" or commonly used machine vision software for reading barcodes and 2D matrix encoding and OCR (Optical Feature Recognition). SherlockProfessional includes all machine vision software tools, especially for multiple camera inspections, with dedicated algorithms and more sophisticated image processing capabilities.
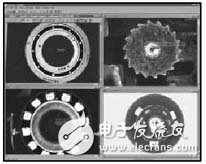
The Sherlock series of products has the same interface, a graphical interface, no need to write new code, as long as a few simple click operations can complete the detection of various applications. The software uses high-performance machine vision algorithms, and the flexible interface allows the corresponding operator interface to be created according to the user's system requirements, enabling a variety of machine vision inspection systems. Figure 4 is the software interface of Sherlock.
The software can extract areas to be processed such as lines, circles, arcs, rectangles, points, etc., and perform image processing on the extracted areas, including logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, add, subtract, enlarge, reduce, and project Such as mathematical operations, convolution, Sobel operations and other image filtering, image folding, rotation, zoom and other processing, and save and store images. Calibrate linear, nonlinear, perspective, and distortion distortion, based on camera or real coordinate calibration, and automatic recalibration. The software can perform edge and point analysis on images, perform pattern recognition such as searching or positioning, measure and measure distance, angle, diameter and circumference, confirm and feedback images, and input and output digital and analog signals.
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigarettesfactory.com
