The neural network of the computer is it! How much do you know about PCI-E?
Will the slots on the motherboard be high-end goods? The answer is not necessarily oh! In particular, the CPU of an ordinary home PC—the guy in charge of controlling the PCI-E channel—can provide a “quantitative†number of PCI-E channels. The extra slots may be a gimmick.
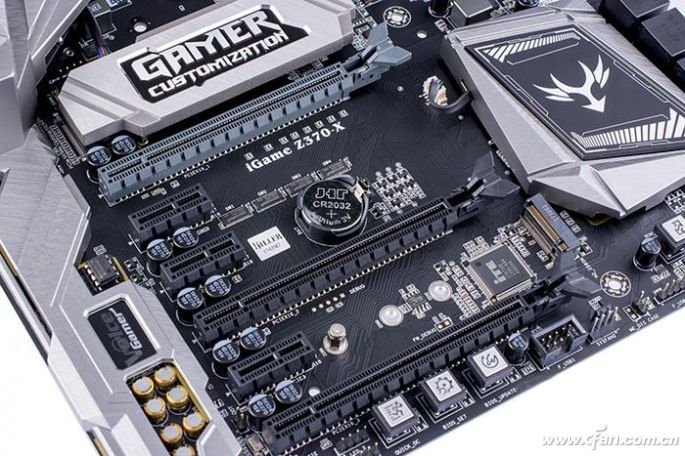
What is the difference between PCI-E slots?
Little friends must have discovered that there are a lot of long PCI-E slots on the motherboard, but there is a particularly short one. Why is this happening? This is because the characteristics of PCI-E bus technology determine - PCI-E is a serial communication system, the so-called shortest kind is PCI-E 1 x, usually the PCI-E slot used for graphics cards is PCI-E E 8×/16×.
The so-called 1× refers to a PCI-E channel. The characteristics of PCI-E are comparable to the traffic lanes of a road, one lane, four lanes, eight lanes, and sixteen lanes. The wider the bandwidth, the higher the transmission speed. This also determines PCI. The -E slot can be designed to have different lengths depending on the usage requirements. Moreover, this flexible design of PCI-E allows it to achieve maximum compatibility. 16× is compatible with 8× (its size is the same), and it can also be backward compatible with 1× and 4× devices, making it more convenient to use. .

In addition, PCI-E as a bus standard also derived a lot of device interfaces, such as USB, SATA, network cards, sound cards, and so on. Of course, each device interface must also be "translated, controlled" by a controller.
By the way, the current PCI-E 4× slot has been difficult to see. Almost all motherboards have only 1× slots and 8×/16× slots, mainly due to the problem of device suitability.
The PCI-E version has huge differences
Understand the difference in the length of the slot, but also know the difference between the version of PCI-E. The current common motherboards are PCI-E 3.0 standard, and the bandwidth is several times faster than PCI-E 1.0.
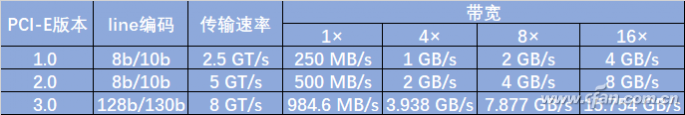
In 2003, the PCI-E 1.0 standard was introduced, with a data rate of 250 MB/s per channel and a transmission rate of 2.5 GT/s. Here to explain, the transmission rate is expressed as the amount of transmission per second, not the number of bits per second, because the transmission volume includes overhead bits that do not provide additional throughput; In addition, PCI-E 1.0 uses 8b/10b encoding scheme, directly occupied 20% of the original channel bandwidth, that is to say the actual use of bandwidth is not up to the nominal value.
By the time the PCI-E 2.0 standard was born in 2007, its transmission rate was increased to 5GT/s compared to PCI-E 1.0. The PCI-E 2.0 standard still uses the 8b/10b encoding scheme, so the effective transmission rate is 4GT/s maximum transmission rate instead of 5G/s.
In response to the problems in the first two versions of the PCI-E standard, 3.0 was introduced in 2010 after being delayed many times. The biggest change is that PCI-E 3.0 will upgrade the encoding scheme from the previous 8b/10b to 128b/130b, while reducing the bandwidth overhead from 20% to about 1.54%. Therefore, the 8GT/s transfer rate bit rate of PCI-E 3.0 effectively provides a bandwidth of 985MB/s per channel, which greatly improves performance. This also benefits high-end graphics cards. The performance of the 3.0-standard PCI-E graphics card has been significantly improved over the past.
Note that the device is the same slot to match the same generation, if it is 3.0 PCI-E bus slot with 2.0 graphics card, then still take the 2.0 standard, in short, the barrel principle, whichever is the lowest.
Who is responsible for controlling PCI-E?
The control PCI-E should have been the Northbridge in the motherboard chipset, but as the CPU integrates the chipset's Northbridge functionality, the job is now controlled by the CPU. For example, at present, most CPU+ motherboards can provide up to 40 PCI-E 3.0 channels (for example: i7-8700K 16 directly connected CPUs, the motherboard PCH chip provides 24 extensions, DMI 3.0 connectivity to the CPU, but the bandwidth is only PCI- E 4×), these channels not only need to be made into PCI-E slots, do not forget that USB, SATA, network cards, sound cards, etc. are all connected to the CPU through the PCI-E channel, so even if the motherboard provides Several PCI-E 8×/16× slots, not all slots can all run at the same time (16×), and some even have only the PCI-E 4× level. After all, the CPU provides 20 PCIs. -E channel, slot and device share these channels only.
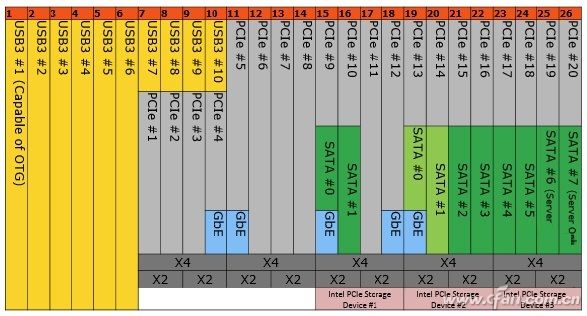
Say so much, just hope that the little partners understand the role and meaning of the PCI-E slot, especially not to let the manufacturers confuse the non-believing full board slot is high-end goods, after all, the total number of PCI-E channels is so much Is nothing more than a shared channel.

Ground Screw For Other Buildings
High Dip Galvanized Ground Screw Pile made of carbon steel :Q235 ,according to standard ;DIN EN ISO1461-1999 ,not only used on the Solar Mounting projects,but also can be use for many other fields ,such as some temporary building,for timber,flage and banner,traffice sign ,for fencing construction ,for container house,for vineyard fencing ,for bridge & . it is easy to install ,no need digging ,no-concrete ,save time and cost .no harm to environment .
Due to their design and ease to installation,they are most commonly used wheneversoil conditons preventstandard foundation solutions,instead of requiring large excavationwork,they thread into the ground.
Construction Ground Screw,Hdg Ground Screw,Screw Anchor,Helical Pier,Ground Screw Anchor
BAODING JIMAOTONG IMPORT AND EXPORT CO., LTD , https://www.chinagroundscrew.com
