A brief description of the stack structure in the ZigBee standard
The ZigBee standard defines a stacking protocol that ensures interoperability of wireless devices in low-cost, low-power, and low-data-rate networks. This article briefly describes the ZigBee stack structure specified in the ZigBee standard.
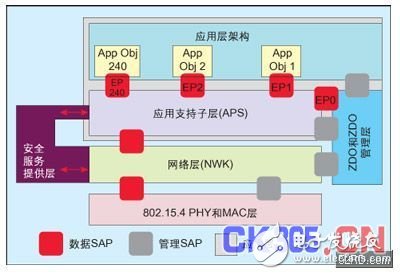
Figure 1: ZigBee stack architecture.
The ZigBee stack is built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and defines the MAC and PHY layers of the protocol. ZigBee devices should include the PHY and MAC layers of IEEE 802.15.4 (which defines RF radio and communication with neighboring devices), and the ZigBee stack layer: Network Layer (NWK), Application Layer, and Security Service Provisioning Layer. Figure 1 gives an overview of these components.
ZigBee stack layerEach ZigBee device is associated with a specific template, which may be a public template or a private template. These templates define the application environment of the device, the type of device, and the clusters used for communication between devices. Public templates ensure interoperability of devices from different vendors in the same application domain.
Devices are defined by templates and implemented as application objects (ApplicaTIon Objects) (see figure). Each application object is connected to the rest of the ZigBee stack through an endpoint, which is an addressable component in the device.
From an application perspective, the essence of communication is the endpoint-to-end connection (for example, a device with a switch component communicates with a remote device with one or more lamp components in order to illuminate these lights).
Communication between endpoints is achieved through a data structure called a cluster. These clusters are containers for all the attributes required to share information between application objects, and clusters used in special applications are defined in the template. Figure 2 is an example of a device and its interface:
Each interface can receive (for input) or send (for output) data in cluster format. There are two special endpoints, endpoint 0 and endpoint 255. Endpoint 0 is used for configuration and management of the entire ZigBee device. Applications can communicate with other layers of the ZigBee stack through Endpoint 0 to enable initialization and configuration of these layers. The object attached to endpoint 0 is called the ZigBee device object (ZD0). Endpoint 255 is used for broadcast to all endpoints. Endpoints 241 through 254 are reserved endpoints.
All endpoints use the services provided by the Application Support Sublayer (APS). APS interfaces with endpoints through the network layer and the security service delivery layer and provides services for data transfer, security and binding, thus adapting to different but compatible devices, such as illuminated switches.
APS uses the services provided by the network layer (NWK). NWK is responsible for device-to-device communication and is responsible for the activities, message routing and network discovery involved in device initialization in the network. The application layer can configure and access network layer parameters through the ZigBee device object (ZD0).
802.15.4 MAC layerThe IEEE 802.15.4 standard defines two layers of the beginning of the OSI model for the Low Rate Wireless Personal Area Network (LR-WPAN). The PHY layer defines the characteristics that a radio frequency should have. It supports two different RF signals, which are located in the 2450MHz band and the 868/915MHz band. The 2450MHz band RF can provide a data rate of 250kbps and 16 different channels. In the 868 / 915 MHz band, 868 MHz supports one channel with a data rate of 20 kbps, and 915 MHz supports 10 channels with a data rate of 40 kbps.
The MAC layer is responsible for single-hop data communication between adjacent devices. It is responsible for establishing synchronization with the network, supporting association and de-association, and MAC layer security: it provides reliable links between two devices.
About service access pointsDifferent layers of the ZigBee stack communicate with the 802.15.4 MAC through the Service Access Point (SAP). SAP is the interface between the services provided by a particular layer and the upper layer.

Figure 2: Device description defined by the template.
Most layers of the ZigBee stack have two interfaces: the data entity interface and the management entity interface. The goal of the Data Entity Interface is to provide the required regular data services to the upper layers. The goal of managing entity interfaces is to provide mechanisms to access internal layer parameters, configuration, and management data to the upper layer.
ZigBee securityThe security mechanism is provided by the security service provider layer. It is worth noting, however, that the overall security of the system is defined at the template level, which means that the template should define what type of security should be implemented in a particular network.
Each layer (MAC, network or application layer) can be protected and they can share a security key in order to reduce storage requirements. The SSP is initialized and configured through ZD0 and requires the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). The ZigBee specification defines the purpose of the Trust Center. A trust center is a trusted device that distributes security keys across the network.
ZigBee stack capacity and ZigBee devicesBased on all the features and support defined by the ZigBee stack, it is easy to speculate that the ZigBee stack implementation requires a large amount of memory resources in the device.
However, the ZigBee specification defines three types of devices, each with its own functional requirements: The ZigBee Coordinator is a device that starts and configures the network. The coordinator can maintain binding tables for indirect addressing, support associations, and design trust centers and perform other activities. A ZigBee network only allows one ZigBee coordinator.
A ZigBee router is a device that supports associations and can forward messages to other devices. A ZigBee grid or tree network can have multiple ZigBee routers. ZigBee star networks do not support ZigBee routers.
The ZigBee end device can perform its related functions and use the ZigBee network to reach other devices that need to communicate with it. It has the least memory requirements.
However, it is important to note that the specific architecture of the network can dramatically affect the resources required by the device. The network topologies supported by NWK are star, tree, and grid. Among these network topologies, star networks have the lowest resource requirements.
Summary of this articleThe ZigBee stack should provide all the features required by the ZigBee specification, so the manufacturer's focus is on developing real-world applications. To make it easier to implement, if the manufacturer uses some kind of public template, then most of the off-the-shelf configurations are available. If you don't have the right public template, you can take advantage of the work that other templates have already done to create your own template.

Knowing which specific Mac model you have is important.
Please contact with me, that I can tell you about your Mac model and generation will be displayed.
macbook 85w charger,apple macbook 85w charger,85w charger for macbook pro
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com
