Building automation control network data communication protocol BACnet
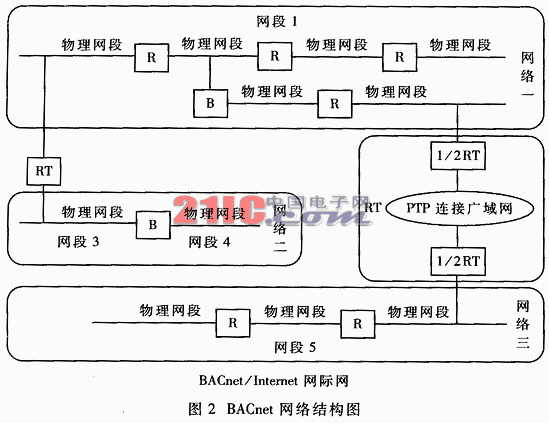
Abstract: An overview of the current status of communication protocols and fieldbuses in intelligent buildings, and a detailed introduction to the new data communication protocol in this field, BACnet. Keywords: BACnet intelligent building automation object-oriented With the rapid development of computer, communication, control and graphic display technologies, that is, 4C technology and the vigorous construction of information highways around the world, intelligent buildings, this combination of digitalization, networking and informationization, have begun to enter people's vision. However, various control functions in smart buildings are becoming more and more powerful and complex nowadays, resulting in devices from different manufacturers used in the same building, but each manufacturer basically develops its own proprietary communication protocol, so various Such communication protocols and equipment bring many inconveniences to the system integration and management of intelligent buildings, and users are in a situation where they are constrained by the manufacturer and the cost, use and maintenance costs increase. Therefore, formulating an open and unified communication protocol standard and forming a plug-and-play environment has become a very urgent problem to be solved. At present, in the field of intelligent buildings, field buses and communication protocols mainly include: (1) bus protocols originally used in the field of industrial control, such as representative Probus, Lonwrks bus, CAN bus, etc .; (2) specifically for intelligent buildings The bus and communication protocol, such as BACnet and CEBus in the United States, EIB in Europe and so on. This article introduces the BACnet in detail. Building Automatic Control Network Data Communication Protocol BACnet (A Data The Standard Project Committee organized by the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air-Conditioning Engineers, 135P, was formally adopted by the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air-Conditioning Engineers in June 1995. It was formally adopted in June 1995. The standard number is ANSI / ASHRAStandard 135-1995. In December of the same year, it officially became the US national standard and was recognized by the European Standards Committee as the draft EU standard. In January 2000, representatives of 15 countries (China, France, Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States, etc.) of the ISO 2005 TC 2005 Committee unanimously passed a resolution to review BACCnet as a "Committee Draft", which was appropriately revised and included in the "International Standard Draft ", And finally became an international standard. General building automation equipment is divided into two parts in terms of function: one part specializes in the control function of the equipment; the other part specializes in the data communication function of the equipment. BACnet is to establish a unified data communication standard so that devices can interoperate. The BACnet protocol only stipulates the rules of communication between devices, and does not involve implementation details. The BACnet protocol model is: (1) All network devices, except those based on the MS / TP protocol, are completely equivalent (peer to peer); (2) Each device is an "object" entity, each Each object is described by its "attributes" and provides a method for identifying and accessing devices in the network; devices communicate with each other by reading / writing the attributes of certain device objects and using the "services" provided by the protocol; (3) The completeness of the device (Sophistication), that is, its ability to fulfill service requests or understand the types of object types, is reflected by the "consistency class" of the device. 1.1 Architecture of BACnet BACnet is an open network protocol for intelligent buildings, following the OSI model architecture. The BACnet architecture hierarchy diagram is shown in Figure 1. The BACnet protocol considers several aspects such as hardware / software implementation, data transmission rate, system compatibility, and network application, and currently supports five types of data link / physical layer specifications. The master / slave / token transfer (MS / TP) protocol is a data link specification specifically designed for building automation equipment. BACnet supports twisted pair, coaxial cable and optical cable on the physical medium. In the topology structure, support star and bus topology. BACnet does not strictly stipulate the network topology, as shown in Figure 2. Among them: the segment (Segment) is a segment interval formed by multiple physical network segments connected by a repeater (R); the network is formed by connecting multiple network segments through a bridge (B), and each network forms a MAC Address domain; BACnet / Internet network is an Internet formed by interconnecting multiple networks using different LAN technologies with routers (RT). The network layer realizes the connection of two or more heterogeneous BACnet LANs (different number chain layers) through "routers", and performs automatic configuration, routing table maintenance and congestion control of "routers" through protocol packets. The connection between the BACnet router and each network is called a "port". The routing table contains the following items of the port: (1) the MAC address and network number of the network to which the port is connected; (2) the list of network numbers that the port can reach the network and the connection status with these networks. In Figure 2, "1/2 RT" is a semi-router, which is connected by PTP to form a complete BACnet router, that is, the BACnet Internet shields the WAN technology to the application layer. The BACnet application layer is the BACnet application entity. It serves the upper layer application program through API (application programming interface) and communicates with the peer application layer entity. The application entity consists of two parts: the user unit and the application service unit (ASE). ASE is a set of application services with specific content. The user unit supports local APIs, saves transaction context information, generates request IDs, records application service responses corresponding to IDs, maintains counters needed for the timeout retransmission mechanism, and maps device behavior requirements to objects. The BACnet application layer provides both certified and unconfirmed services. BACnet defines four service primitives: request, indication, response and confirmation, which are transmitted through the application layer protocol data unit (APDU). Since BACnet is built on a connectionless communication mode, the simplified function of the transport layer part of the end-to-end service provided by the OSI model is also implemented by the application layer. They are: reliable end-to-end transmission and error checking; Flow control; message reassembly and sequence control. 1.2 Objects, services and functional groups of BACnet BACnet uses object-oriented technology to provide a standard for representing building automation equipment. In BACnet, an object is a set of data structures transmitted between network devices. The network devices achieve interoperability by reading and modifying the object data structure encapsulated in the application layer APDU. BACnet currently defines 18 objects. As shown in Table 1, each object must have three attributes: object identifier (Object_Idener), object name (Object_Name), and object type (Object_Typ). Among them, the object identifier is used to uniquely identify the object; the BACnet device can establish the contact with the device containing the related object by broadcasting the object name of an object contained in itself. The BACnet protocol requires that each device must contain a "device object". By reading its attributes, the network can obtain all the information of the device.
In BACnet, the method of an object is called a service. The object and its attributes provide an abstract description of the "network visible information" of a building automation device, and the service provides commands and methods of how to access and manipulate this information. BACnet devices implement services by transmitting service request and service response messages in the network. BACnet defines 35 services and divides them into 6 categories: (1) Alarm and Event Services (Alarm and Event Services) contains 8 types of services to deal with changes in the state of the environment, and provides notification of changes in BACnet device preset request value changes 2. Request alarm or event status summary, send alarm or event notification, receive alarm notification confirmation, etc .; (2) File Access Service (File Access Services) includes 2 services, providing methods for reading and writing files, including upload / download control The capabilities of programs and databases; (3) Object Access Services (Object Services) contains nine services, providing methods for reading, modifying, and writing attribute values, and adding and deleting objects; (4) Remote Device Management Service (Remote Device Service) Contains 11 kinds of services, provides tools for maintenance and fault detection of BACnet equipment, Methods; (5) Virtual Terminal Services (Virtual Terminal Services) contains three services and provides a character-oriented data bidirectional exchange mechanism, making other building automation devices with proprietary features a BACnet virtual terminal and enabling BACnet networks Reconstruct it; (6) Network Security Services (Network Security Services) contains two services that provide peer entity verification, data source verification, operator verification, and data encryption. The BACnet function group specifies the combination of objects and services required to implement specific control functions. BACnet has defined 13 functional groups, including clock functional group, event response functional group, file functional group, virtual terminal functional group, device communication functional group, etc. 1.3 Description of BACnet equipment level and equipment level In the actual building automation system, it is not necessary and impossible for all equipment to support and contain all the above-mentioned objects and services. Therefore, BACnet has defined six consistency categories (device level). The classification number of the consistency category is 1 to 6, and the lowest level is category 1. Each category stipulates the minimum service subset to be implemented by the device, and includes all services at a low level. In order to help users and engineering staff determine the interoperability between different BACnet devices, manufacturers are required to provide standard format files for each device to identify the content of the BACnet standard that has been implemented in the device, that is, the file must include instructions that the device meets the BACnet level. This file is called PICS (Protocol Improving Control Center), and it includes: (1) Basic information that identifies the manufacturer and describes the device; (2) The device complies with the level of BACnet; (3) The functional group supported by the device; (4) Supported standards-based or proprietary services, the device's ability to initiate or respond to service requests; (5) Standard-based or proprietary object types and attribute descriptions supported by the device; (6) Data link technologies supported by the device; (7) Segment request and response supported by the device. 2 Internet expansion of BACnet Currently, the BACnet standard uses two technologies to achieve interconnection with Internet. The first technology is called "tunnel" technology in Annex H, and its equipment is called packet packaging / disassembly equipment, or PAD for short. Its role is like a gateway / router, which is shown in Figure 2 where two half routers are connected to the WAN to form a complete BACnet router. The second technology is called BACnet / IP in Annex J. The device directly encapsulates the IP frame / packet and transmits it on the BACnet network and Internet. The PAD encapsulates the BACnet message data in an IP protocol data packet for transmission, and decapsulates the destination BACnet network. Therefore, every BACnet network connected to Internet must be equipped with a PAD gateway / router. It can be a separate device or part of the function of a building control device. Ashrae officially released Annex J in January 1999 and became an American national standard. It standardizes the technology that supports TCP / IP equipment to form a BACnet network, and is called BACnet / IP network, or B / IP for short, which is a collection of one or more IP subnets, with a single BACnet network number as a whole. The BACnet / IP network message is an IP packet at the network layer and a UDP datagram at the transport layer, so as to achieve the integration with Internet TCP / IP protocol. Open, compatible, flexible, widely supported and specifically targeted at intelligent building communication protocols or field buses will surely become a development direction in the field of intelligent building. The BACnet protocol is such a pioneering technology that enables devices of different manufacturers to be interconnected, interchanged, and interoperable to create a seamlessly connected (seamless linking) building automation system that fully satisfies owners, users, and integrators It also provides a variety of network interconnection and Internet access solutions, which provides convenient conditions for the integration of various systems within the intelligent building, making it easy for the intelligent building to take the information highway. |
Integrated Led Lamp,Integrated Led Lights,Integrated Panel Lamp,Integrated Led Ceiling Lights
Changxing Fanya Lighting Co.,Ltd , https://www.fyledlights.com