Detailed analysis of early, present and future memories
Today, the storage capacity commonly used on our computers is basically a few hundred G. Even small MP3 players and other handheld devices are usually several Gs. But decades ago, such a large amount of storage could only appear in science fiction. Sometimes, we will take it for granted that today's hard disk storage should be so large, but it is not. Below we will introduce you to the storage devices that may be popular in the early, present and future.
Mercury delay line
In 1950, the world's first computer with stored program functions, EDVAC, was designed by Dr. von Neumann. Its main feature is the use of binary, the use of mercury delay lines for memory, instructions and programs can be stored in the computer.

In March 1951, the first universal automatic computer UNIVAC-I designed by ENIAC's main designers, Mokley and Eckert, was delivered. It can be used not only for scientific calculations, but also for data processing.
Selection tube
The selection tube is an electronic storage device that appeared in the middle of the 20th century. It is a device that converts from intuitive storage to machine storage. In fact, the perforated tape storage that appeared in the 19th century was a product of direct storage to machine storage. He accelerated the shutdown of a census in a western country in the 19th century.

The capacity of the selection tube ranges from 256 to 4096 bits. The 4096-bit selection tube is 10 inches long and 3 inches wide. It was originally developed in 1946 because it is too expensive and not widely used.
Perforated card / perforated tape
Punch cards are information input devices for early computers that typically store 80 columns of data. Punch cards were popular in the mid-1970s. We should note that punch cards are more likely than computers. Its history can be traced back to the textile industry in 1725 for mechanized weaving machines.
Speaking of punch cards, I have to talk about the founder of IBM, Professor Hermann Hollers, who invented the automatic tabulator in 1888, the first data processing machine using punch card technology. Automatic tabulators were used in the 1890 and subsequent US Census and were a huge success
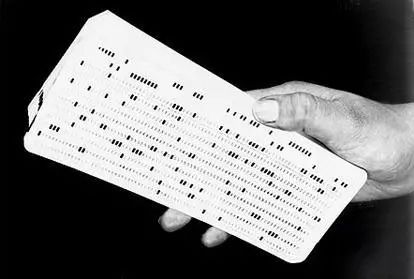
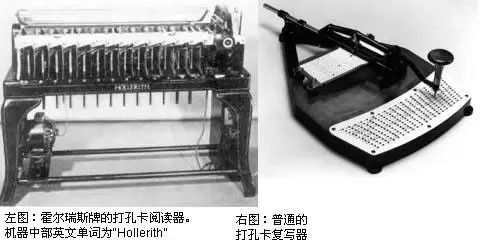
Figure 2-7a is a schematic view of a perforated card with holes penetrating at certain locations in the card, and the data stored in the punched card can be read by the photoelectric conversion device. Perforated tape is similar to punched cards, but is easier to store. Perforated tapes are stored in a similar way to punched cards, and each row can store one character. Figure 2-7b shows a paper strip with 8 holes per row.

Drum memory
In the 1950s, the drum was applied as an internal memory to the IBM 650. In the subsequent IBM 360/91 and DEC PDP-11, the drum was also used as swap area storage and page storage. A representative product of the drum is the IBM 2301 fixed head drum memory.
The drum is magnetically coated with a magnetic material coated on the surface of the aluminum drum to store data. The drum rotates at a high speed, so the access speed is fast. It uses saturation magnetic recording, from fixed heads to floating heads, from the development of magnetic glue to continuous magnetic media using electroplating. These have laid the foundation for later disk storage.
The biggest disadvantage of the drum is that the storage capacity is too small. A large cylinder has only one surface for storage, and both sides of the disk can be used for storage, which is obviously much more efficient. Therefore, when the disk appears, the drum is eliminated.
The picture below is a picture of a drum. The drum used on the IBM 650 computer is 16 inches long and has 40 tracks. It can rotate 12,500 rpm and can store 10 KB of data.

Tape storage
For the first time, UNIVAC-I used a tape drive as an external memory. First, the parity method and the dual operation circuit were used to improve the reliability of the system, and the first automatic test was performed.
Tape is one of the most common storage media for storing information in all memory devices with the lowest cost, largest capacity, and highest standardization.
It has good interchangeability and is easy to save. In recent years, due to the adoption of high error correction coding technology and write-read channel technology, the reliability and read/write speed of tape storage have been greatly improved.
According to the working principle of read and write tapes, it can be divided into spiral scanning technology, linear recording (data stream) technology, DLT technology and relatively advanced LTO technology.
The tape library is a tape-based backup system that provides the same basic automatic backup and data recovery features, but with more advanced technical features.
Its storage capacity can reach hundreds of PB, it can realize continuous backup, automatic search for tape, and can realize intelligent recovery, real-time monitoring and statistics under the control of drive management software. The entire data storage backup process is completely free from manual interference.

Not only does the tape library have a much larger amount of data storage, but it also has unparalleled advantages in terms of backup efficiency and manual footprint. In the network system, the tape library can form a network storage system through a SAN (Storage Area Network) system, which provides a powerful guarantee for enterprise storage, and it is easy to complete the remote number.
According to access, data storage backup or multi-tape backup through tape mirroring technology, it is undoubtedly a good storage device for large network applications such as data warehouse and ERP.
Dynamic random access memory DRAM
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) was invented in 1966 to store information by capacitors; charged capacitors represent 1, and uncharged represent 0, and the so-called "dynamic" does not mean what is internal, but rather Capacitors will eventually lose their charge and must be refreshed periodically.

Synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) was limited in the 1970s, but it was widely adopted in 1993. Until then, RAM was able to change the input data as quickly as possible, while SDRAM was based on computers. The pulse is adjusted when the data is stored, which allows the data to be distributed to different banks, so that several memory tasks can be executed simultaneously.

Erasable programmable read only memory EPROM
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM) was developed by Intel's Dov Frohman in 1971. This type of memory is non-volatile, meaning that the state of the memory does not change despite the power being turned off. This memory chip is electrically programmable and the information can be erased when exposed to UV light.
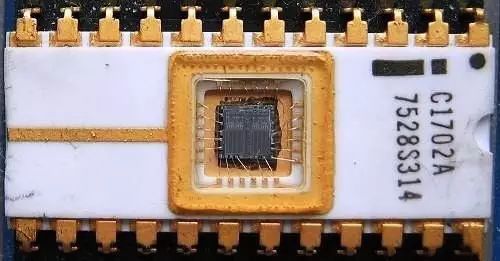
The first EPROM Source developed by Intel in 1971: Wikipedia
Floppy disk storage
The floppy disk was also invented by IBM in 1969 and was popular in the mid-1970s to the early 21st century. The first floppy disk is 8 inches, followed by 5.25 inches and 3.5 inches. The first floppy disk was released in 1971 and has a capacity of 79.7KB. It is read-only. Read-write floppy disks came out the following year.
The trend of floppy disks is that the diameter of the disk is getting smaller and smaller, while the capacity is getting larger and larger, and the reliability is getting higher and higher. The following figure shows three typical floppy disks, where a is a floppy disk with different appearance sizes, and the 3.5-inch floppy disk in b has a capacity of 1.44 MB, which was once widely used as the main mobile storage medium.

In the late 1990s, a 3.5-inch floppy disk with a capacity of 250MB appeared, but it has not been widely used due to compatibility, reliability, cost, etc., and it is difficult to find it now.
Hard disk storage
The world's first hard disk storage was invented by IBM in 1956 and is modeled after the IBM 350 RAMAC (Random Access Method of Accounting and Control). The system has a total capacity of only 5MB and uses a total of 50 24-inch diameter disks.
In 1968, IBM proposed the "Winchester/Winchester" technology, the main point of which is to seal all the high-speed rotating disks, magnetic heads and their seek mechanisms in a dust-free enclosure to form a head-disk assembly ( HDA), isolated from the external environment, avoids dust pollution, and uses a miniaturized light buoyancy head slider, the surface of the disc is coated with lubricant, and the contact starts and stops. This is the prototype of most modern hard drives.

In 1979, IBM invented the thin film magnetic head, which further reduced the weight of the magnetic head, enabling faster access speeds and higher storage densities. In the late 1980s, IBM made another major contribution to the development of memory devices.
Invented MR (Magneto Resistive) magnetoresistive heads, which are sensitive to signal changes when reading data, making the storage density of the discs several tens of times higher than in the past. In 1991, IBM's 3.5-inch hard disk used MR heads, making the capacity of the hard disk reach 1GB for the first time. Since then, the hard disk capacity has entered the order of GB.
IBM also invented the signal reading technology of PRML (Partial Response Maximum Likelihood), which greatly improved the sensitivity of signal detection, thereby greatly increasing the recording density.
At present, the surface density of the hard disk has reached more than 100Gb per square inch, which is a storage device with the largest capacity and cost performance. Thus, in the external storage devices of computers, no other storage device has been able to challenge its dominance in recent years.
Hard drives are not only used in a variety of computers and servers, but are also the basic storage unit in disk arrays and various network storage systems. It is worth noting that the emergence and rapid development of micro hard disks in recent years provides an ideal storage medium for mobile storage.
In the field of large-capacity mobile storage that flash chips can't afford, micro-drives can make a big difference. The current size of a 1-inch hard drive has a storage capacity of 4GB, and a 10-inch hard drive with a 10GB capacity will soon be available. Micro hard drives are widely used in digital cameras, MP3 devices and a variety of handheld electronic devices.
Seagate produced the first 5.25-inch hard disk drive (HDD) in 1980. The look of this storage device is not far from what we are seeing now;
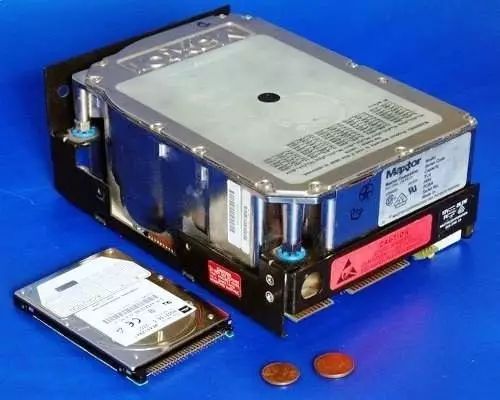

But the first 1GB hard drive, also introduced by IBM in 1980, was a huge monster weighing 550 pounds.

Electrical erasable programmable read only memory EEPROM
Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) was born in 1978. It outperforms the advantages of Electrical Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM), which is programmable and audible in use. The disadvantage is that the number of repeatable programming is limited, but its read and write performance has been getting more and more improved today.
Optical disc storage
Discs are mainly divided into read-only discs and read-write discs. Read-only refers to the content on the disc is fixed, can not be written, modified, can only read the contents. The read-write type allows people to modify the contents of the disc, erase the original content, and write new content. The optical discs for microcomputers mainly include CD-ROM, CD-R/W, and DVD-ROM.
In the 1960s, researchers at Philips in the Netherlands began using laser beams for recording and reproducing information. In 1972, their research was successful and was launched in 1978. The original product was the well-known Laser Vision Disc (LD) system.

From the birth of LD to the CD-ROM for computers, it has gone through three stages, namely LD-laser disc, CD-DA disc, CD-ROM. The following is a brief introduction to the product features of these three memory devices. The LD-laser disc, commonly known as the LCD, has a large diameter of 12 inches and can record information on both sides, but the signal it records is an analog signal.
The processing mechanism of the analog signal means that the analog television image signal and the analog sound signal are subjected to FM (Frequency Modulation) frequency modulation, linear superposition, and then subjected to limiting amplification. The clipped signal is represented by a pit length of 0.5 microns wide.

Although the CD-DA compact disc LD has been successful, its development and production have been plunged into expensive capital investment since it was not developed in advance. In 1982, the Red Book standard for CD-DA compact discs was developed by Philips and Sony.
Thus, a new type of laser disc was born. The CD-DA laser disc recording method is different from the LD system. The CD-DA disc system first performs PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) digitization processing on the analog acoustic signal, and then records it by EMF (8 to 14-bit modulation) encoding. On the plate. The advantage of digital recording instead of analog recording is that it is insensitive to interference and noise, and errors due to defects, scratches or contamination of the disc itself can be corrected.
After the success of the CD-DA system, Philips and Sony naturally thought of using CD-DA as a large-capacity read-only memory for computers. However, to use CD-DA as the memory of the computer, two important problems must be solved, namely, the data structure of the disk suitable for reading and writing by the computer, and the CD-DA error rate must be reduced from the existing 10-9 to 10. -12 or less, thereby producing the Yellow Book standard of the CD-ROM.
The core idea of ​​this standard is that the data on the disk is organized in the form of data blocks, each with an address, so that the data on the disk can be quickly found from hundreds of megabytes of storage space. In order to reduce the bit error rate, a scheme of adding error detection and error correction is adopted.
The error detection uses a cyclic redundancy detection code, the so-called CRC, and the error correction uses a Reed Solomon code. The Yellow Book established the physical structure of the CD-ROM, and in order to make it fully compatible on the computer, the CD-ROM file system standard, ISO 9660, was later developed.
In the mid-1980s, optical disc memory devices developed very fast, and new varieties such as WORM discs, magneto-optical discs (MOs), and phase change discs (PCDs) were introduced. In the 1990s, DVD-ROM, CD-R, CD-R/W, etc. began to appear and spread, becoming the standard storage device for computers.
The optical disc technology is further developed to a high density, and Blu-ray discs, multi-layer multi-step discs and holographic storage discs are being introduced to the market in a short period of time.
Flash memory
Flash memory was developed around 1980, but it was not officially released until 1988; this memory is technically an EEPROM, but it is a big step in speed. There are currently two kinds of flash memory on the market, one is NAND, the other is NOR, the main difference is the difference of logic gates; this memory has spawned a small flash drive, Memory Card.

The chip on the left of the figure is the flash memory, and the memory chip on the right is the memory control chip.
JDEC released the universal flash storage (UFS) specification in 2012. In addition to the power-saving features, the new specifications can also achieve up/down synchronization of 300 Mbit/s.

Toshiba flash memory chip with UFS specification
DDR SDRAM
The industry standard organization JEDEC defined the double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR SDRAM) specification in 2000, as its name points out. In certain cases, this RAM can achieve twice the size of the general SDRAM. Data rate. The DDR SDRAM specification evolved to the second generation, 2003 DDR2, which doubled in speed; in 2007, it doubled the speed, or DDR3.
If the speed is increased by eight times, you are not enough. The latest DDR4 data access speed is doubled, and the innovative architecture design is expected to reduce power consumption.

Corsair DDR-400 memory module with integrated heatsink
Nano memory
In 1998, the University of Minnesota and Princeton University produced successful quantum disks, which are nano-array systems composed of magnetic nanorods. A quantum disk is equivalent to our current 100,000 to 1 million disks, and energy consumption is reduced by 10,000 times.
In 1988, the French first discovered the giant magnetoresistance effect. By 1997, nanostructured devices using the giant magnetoresistance principle had been introduced in the United States. It has broad applications in magnetic storage, magnetic memory, and computer read/write heads. prospect.
In September 2002, the research team at the University of Wisconsin announced that they had developed atomic silicon memory materials by manipulating individual atoms at room temperature, which stored information at a density of 1 million times that of current optical discs. This is a major advance in the research of nano-storage materials technology.
According to a study published by the group, new memory materials are built on the surface of silicon materials. The researchers first sublimed the gold element on the surface of the silicon material to form a precise atomic orbital; then the silicon element was sublimated and arranged in the above atomic orbital;
Finally, silicon atoms are extracted from these aligned silicon atoms by means of a probe of a scanning tunneling microscope. The evacuated portion represents "0" and the remaining silicon atoms represent "1", which is equivalent to An atomic memory material that functions as a computer transistor.
Single Mining Power Supply 2000W
Features
1. Low noise, low ripple, high efficiency
2. The long life cycle averages above 100KH hours
3. 14CM double-rolling fan, good noise, fast heat dissipation
4. Possess complete protection function: over voltage, under voltage
Specification:
Product name: 2000W miner power supply
Input voltage: AC 180V~240V
Support graphics card: 8
Colour: Black
Size: 15 x 14 x 8.6cm
Rated power: 2000W
Maximum power: 2000W
The package includes:1 x miner power supply
Price better, Quantity more, strong factory support for wholesale buyer.
if you need 90V-120V power supply, please contact us.
we can provide Customized power supply with 110V-240V if you need 1800W 2000W 2600W 3300W mining power supply, please feel free to contact us.
mining psu,psu for mining,mining rig psu,power supply,power supply for pc
Easy Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxpcelectronicgroups.com
