Detailed Analysis of Neglected Problems in the Design of Access Control System
The access control system is a popular name for the entrance and exit control system. It is a measure to control and manage the flow of people and goods. In the usual design and application, the control of the access control system is only comprehensive enough for the target personnel. In the Ministry of Public Security GA/T394 -2002 "Technical Requirements for Access Control System" and National Standard GB50396-2007 "Engineering Design Specification for Entry and Exit Control Systems" require that the system must have four basic elements: release, rejection, recording, and alarm. The access control system is called an active prevention system in the prevention of security technology. The system not only can effectively confirm the flow of personnel and articles, but also can quickly complete the identification and judgment, and issue “release†in time. Or “reject†instructions, and all incoming and outgoing information is recorded and saved. If the system is threatened and destroyed, the system should also have its own protection and alarm functions.

In the national standard GB50396-2007 "Engineering Design Code for Import and Exit Control System", five articles are compulsory, and the requirements must be strictly enforced. However, in the actual project design, the following problems are easily overlooked, and even cause serious defects in the system.
Equipment selection and system anti-destruction and anti-technical opening requirementsThe system design should select the equipment of the entrance and exit control system according to the safety level requirements of the project. Here mainly refers to the protection capability of the system, especially the anti-destructive capability and anti-technical opening capability of the equipment used for the protective surface. In GB50396-2007 "Outline Control System Engineering Design Specification" national standard, the protection capability of system equipment is divided into three levels: A, B and C from low to high. However, it must be pointed out that many people mistakenly understand "anti-vandal" as "anti-device destruction." The correct one should look at the ability of the entrance and exit to be unlocked when the equipment on the protective surface is subjected to a destructive attack. For example, the card reader installed on an entrance and exit protection surface was completely damaged after a devastating attack in 1 minute, but within 30 minutes, the destroyer failed to open the entrance and exit. The other is located on the entrance and exit protection surface. It is a very sturdy integrated access control machine. It took the intruder to take 10 minutes to destroy it, but then it took only 1 minute to open the entrance. This means that although the appearance is very strong, the latter's anti-destructive ability is not as good as the former. In the actual application design, the system and products should be selected according to different security levels and management requirements to meet the requirements of “anti-vandal†and “anti-technical openingâ€. In particular, it is necessary to use the identification and control as one of the access control machines, including some fingerprint machines whose RESET button is exposed on the protective surface. As long as someone breaks, use a fine needle to gently click, all stored information will be cleared.
Control equipment installation location and system's own security levelThe mandatory provisions of GB50396-2007 "Engineering Design Code for Import and Exit Control System" clearly stipulate the installation position of the equipment. Article 2 of Article 6.0.2 states: Control and control of the execution part using non-coded signals The equipment must be placed in the corresponding controlled area, the same level controlled area or the high level controlled area of ​​the entrance and exit.
Because in the design of the entrance and exit control system, the multi-door access controller is often used, that is, one controller can control multiple card readers, such as two-door card reader, four-door card reader, and eight-door card reader. Wait. However, it is easier to relate to the installation level of the multi-door controller, which is more likely to involve the security level of the system itself. Please see Figure 1:
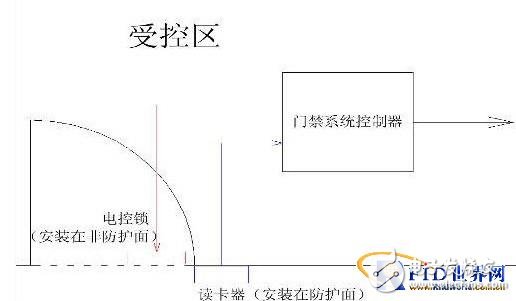
Figure 1 shows the installation position of a standard single access control system. Due to the characteristics of the access control system itself, in most cases, the card reader can only be installed outside the controlled area, outside the protective surface, and its controller and power. The control locks should be designed and installed in the controlled area. The equipment is on the non-protective surface and will not be directly exposed and easily damaged. But when designing a multi-door controller, how should it be determined?
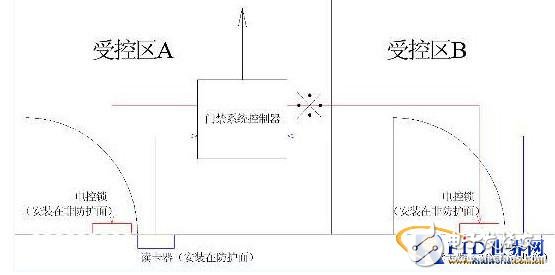
Figure 2 shows a two-door controller for controlling the access of Zone A and Zone B. When Design Zone A and Zone B are controlled zones of the same level, the controller can be installed in Zone A or Zone B. However, when the two zones A and B are required to be independent controlled zones of different levels, the controller has hidden dangers no matter which zone is designed. This is because the current controller basically uses non-encoded signals such as DC or pulse signals to directly drive the electronically controlled locks. Therefore, when the controller is designed to be installed in Zone A, Zone B is not safe; otherwise, it is designed to be installed in Zone B. Area A is not safe. Figure 2 shows that ※ is the weakest point that is most vulnerable to attack.
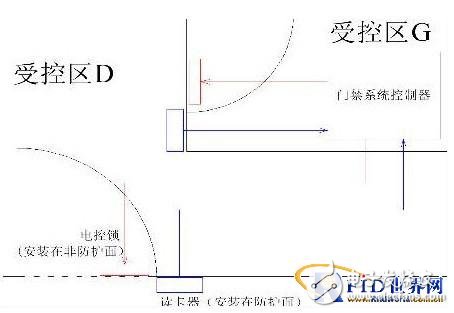
If you want to design a zone with a higher level of security, then Figure 3 is visible and the controller should be designed to be installed in the high-level G zone.
Figure 4 is a comprehensive design case of the entrance and exit control system. The A, B, and E areas are studios. The staff can enter the A area or the B area and the E area, all of which are the same level control area. Design and install a multi-door controller in Area B; Areas C and D are non-same independent control areas, which are responsible for the entry and exit management of chemicals and data files, so they cannot be shared and installed in Area B in Area C. The controller can only design one controller separately in the C area. Zone D is connected to the laboratory, and the laboratory has designated the G zone as the highest-level core laboratory. This allows a multi-door controller to be designed to control the G, F, and D zones in the G zone. Of course, testers who can enter the F zone may not be able to enter the core test room of the G zone; otherwise, personnel who can enter the highest G zone will be able to enter the F zone. The control of zone D comes from the controller installed in the most advanced zone G, so the security level of the zone is not affected.
Lithium Polymer Battery,Charger For Lithium Ion Battery,Lithium Ion Battery 24V,Polymer Lithium BatteryPolymer lithium battery
Langrui Energy (Shenzhen) Co.,Ltd , https://www.langruibattery.com
