Hybrid coaxial / wireless multimedia home network using 802.11 technology
Hybrid coaxial / wireless multimedia home network using 802.11 technology
Wireless home networking has become the favorite technology for home data distribution services. The price of 802.11b is very close to that of wired products. They do not need to install new lines or use old lines to bring connectivity to every corner of the home. It has become the most natural choice for users to set up a home network. The huge demand for 802.11b products in the enterprise market not only drives down costs, but also allows consumers to use home and enterprise networks through the same interface, which makes 802.11b a more attractive home network technology.
Consumers hope that multiple computers in the home can share a broadband line, which has become the main driving force for the growth of home networks. 802.11b provides 11 Mbps data rate and 300-500 feet of online distance, an excellent solution to meet this demand. As more new services appear on the home network, the 802.11g / a standard that is introduced later can meet the increasing transmission capacity requirements. 802.11e and 802.11i comply with more stringent network connection quality (QoS) and transmission security regulations. However, as the demand for transmission capacity of home networks continues to increase, the capabilities of operators may be limited by the coverage of wireless communications, preventing them from providing new high-bandwidth services and applications, such as video distribution in the home. Although the most advanced 802.11a / g standard provides up to 54 Mbps data output, which is enough to distribute multiple MPEG video streams at home, but products developed according to these standards, even in the highest output operating mode, their transmission distance or Coverage is still insufficient in many situations. The 802.11a / b / g high-output operation mode is most susceptible to various factors, such as transmission path loss caused by obstacles and fading caused by time-varying multiple paths. They make these The operation mode cannot guarantee the reliable transmission service.
This article will introduce a new concept, which can help the industry solve the problem of coverage and bring high frequency bandwidth service to every corner of the home, especially video distribution. We recommend using the in-home coax network as the backbone line of the wireless home network, and then using 802.11 a / b / g as the transmission protocol for the coaxial line.
Using the home coaxial network to increase the distance and coverage of the wireless network, the industry can provide reliable home video distribution and other services, ensure that the high-capacity transmission range covers every corner of the home, and enjoy 802.11b / a / g / e / All advantages brought by i, including QoS, security and low cost.
Overall concept
We recommend a home network that is based on 802.11 transmission over the air and coaxial cables (in this article, "802.11" refers to all standards based on 802.11, including 802.11a, (b, g, e and i extended standards). Figure 1 is a basic block diagram of a hybrid wireless / coaxial 802.11 network, including a base station (AP) and antennas used in a wireless 802.11 home network, and a coaxial line; this network also includes two workstations (STA): one through the same The axis cable is connected to the network, and the other is connected to the network through wireless communication. Among the multiple nodes of the home coaxial network, one node will be connected to the wireless bridge / repeater through the coaxial cable.
Each packet generated by the base station can be transmitted through wireless communication or coaxial cable, which means that each packet may reach the end through three signal paths: the first path is the direct wireless established by the base station antenna Link; the second path is to reach the repeater through the coaxial cable, and then wirelessly transmitted to the wireless workstation; the third path to the destination via the coaxial cable. Whether through wireless communication or coaxial cable, all transmissions will use the 2.4GHz band (that is, the band used by 802.11 b and g).
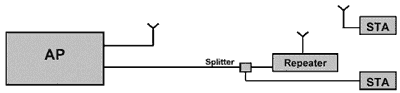
figure 1
In most homes, if the 2.4 GHz band signal of 802.11b / g is transmitted via coaxial cable, its propagation loss is usually lower than that of wireless communication transmission-if wall barriers or other wireless signal transmission obstacles are considered, This phenomenon will become more apparent. Therefore, coaxial lines can be used to expand the connection distance and coverage of the network. We only need to use low-loss coaxial paths or hybrid coaxial / wireless paths to bypass certain higher-loss wireless paths; coaxial network base The full coaxial path between the station and the workstation also provides extremely high transmission quality. 802.11g also has a very reliable operating capability in the highest output mode (54 Mbps).
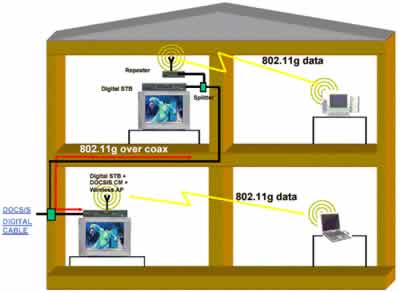
figure 2
Fig. 2 is an application example of a general family. The home in this example uses 802.11g to distribute data and video. The digital set-top box on the first floor contains an integrated DOCSISTM cable modem and an 802.11g base station. The data rate is up to 54Mbps; there are two computers at home sharing a broadband line. They will surf the Internet and send and receive e-mail via wireless communication. The computer on the first floor is connected to the set-top box / base station through 802.11g wireless communication, and the second computer is located on the second floor. It may have exceeded the wireless signal coverage of the set-top box, so it must be through the coaxial / wireless on the second floor. The repeater is connected to the network, and this repeater can expand the coverage of the wireless network. In this example, the computer on the second floor can also be connected to a wireless network, which is one of the main advantages of a hybrid coaxial / wireless network.
The second important advantage is the establishment of a high-capacity connection between two set-top boxes at home, allowing video signals to be sent from one room to another. Although the distance between the two rooms still allows 2-11 Mbps wireless rate, which is sufficient to support data transmission services such as Internet access and email sending and receiving, video distribution requires 54Mbps data output, which must be achieved through the coaxial line between the two set-top boxes . The high-capacity line between the two set-top boxes can be used to share the video content recorded by the personal video recorder, and consumers can also send and receive e-mail or access the Internet through any set-top box. The set-top box with built-in base station function can be used as a home media center to provide stored audio and video content. Other set-top boxes with fewer functions can access this information through the coaxial network; in addition, all set-top boxes can use the home Data services and computer resources, such as printers, scanners, and cameras.
The 802.11e QoS capability will ensure the efficiency of the use of these shared media. It can also ensure that the appropriate bandwidth is configured for services that require QoS, and the delay time is limited to a certain range. The CableHomeTM function provided by the set-top box can help manage the home network .
By combining a high-capacity coaxial line with 802.11e, companies can provide stable and reliable high-frequency bandwidth services between coaxial network workstations, such as video distribution.
Technical considerations for hybrid coaxial / wireless networks
Although all parts of the home coaxial network are designed for signals below 900 MHz, 802.11 signals can carry the attenuation caused by operations in the 2.4 GHz band. Each meter of the coaxial cable will cause 0.5dB signal attenuation, and the attenuation of the common signal splitter will also reach 20-30 dB (2.4 GHz signal measurement results at the input and output ends of the splitter). Requirements are not as strict as good wireless channels. Existing 802.11b / g systems can tolerate 90-100dB attenuation between the transmitter and receiver (while still providing high data output), which can provide a sufficient line attenuation budget (attenuaTIon budget), enough to support hundreds Feet of coaxial cable and multiple splitters.
The hybrid coaxial / wireless network introduces the problem of multiple paths, because some cables and splitters may not provide terminal matching; but even so, in the face of various reflections and signal transmission paths in a typical wireless environment, 802.11 components The special design can reduce serious multi-path problems. 802.11 also contains inherent security protection functions, which can solve the security concerns caused by the overflow of the signal into the neighbor's home.
Comparison of various solutions
In order to solve the problem of distributing multimedia content at home, manufacturers provide cable TV operators with many solutions. The following is a comparison of these solutions and the solutions proposed in this article:
1. Analog DistribuTIon
For the problem of home video distribution, analog distribution can provide a simple solution. Its unique advantage is that it does not need to use another signal converter for the decoding of upconverted video. The function of this solution Both the quality and the quality are limited, requiring separate lines and additional parts to transmit various data including remote control data. Micro-reflecTIons of copper shaft lines will also make the picture quality worse. 802.11 digital signals have stronger resistance to micro reflections, so they can provide stable and reliable video and high-speed data transmission services through the home coaxial network.
2. Pure 802.11 a / b / g + e network
Although in most cases, this kind of network can provide a connection range covering the entire family, and its rate is sufficient to support broadband line sharing, and bring data services to every corner of the home, but it is possible to provide multimedia distribution services Still insufficient. High-output operating modes are most susceptible to wireless path loss and multi-path. Operating modes that are capable of supporting video distribution may not provide complete coverage.
We can use wireless repeaters to extend the support distance of the network. Although repeaters can extend the coverage (at the cost of using additional bandwidth), without careful planning, it still cannot guarantee full coverage; in addition, Compared with the hybrid coaxial / wireless network proposed in this article, this solution is less robust and more expensive.
3. HPNA and HPNA (HPNA over cable)
As a home networking technology, HPNA 2.0's market performance was unsuccessful. Although its data rate was sufficient to support high-speed data services, it lost to other more popular wireless technologies while competing for market share. Affected by the location of the telephone socket, it cannot provide complete coverage; for many users, using a telephone line as a home network is not as straightforward as using wireless technology. In fact, the number of component and system vendors developing 802.11 solutions has increased substantially, while the number of component and system vendors developing HPNA products has been steadily decreasing, making this technology less attractive because of lack of competition.
HPNA 2.0 is completely unsuitable for multimedia applications, its actual data rate is not sufficient to support video distribution, and there are very few QoS mechanisms in the specification. Not only is the use of shared media inefficient, the industry is also unable to provide the services needed for charging QoS online quality assurance; although the new generation HPNA3.0 standard may solve this problem, it still has many other problems, which makes HPNA 2.0 unable to become an attractive home network technology.
Some manufacturers also recommend the use of cable TV HPNA 2.0, the method of which is similar to the recommendations for wireless connections in this article; but unlike the 802.11g / a standard that provides high-speed mode and QoS functions, HPNA 2.0 cannot distribute multiple MPEG strings through cable TV lines Stream, because of its insufficient data output, also lack of QoS function.
Due to the overlapping of the HPNA 2.0 frequency band and the cable TV's upstream frequency band, the cable TV HPNA needs up-conversion functions to avoid interference with the cable TV's upstream transmission, but this will introduce non-standard components into the solution and force it to use the telephone line HPNA Parts other than solutions; in addition, to support multi-vendor interoperability, it needs another set of standards. Frequency conversion may also cause problems for standard HPNA parts, because HPNA2.0 does not support this conversion. These problems, coupled with the fact that there are few HPNA 2.0 component manufacturers, make such solutions basically manufacturer-specific solutions.
Not only that, in order to bridge the coaxial network and the telephone network together, the coaxial line and the telephone line must meet somewhere in the home; but in many homes, the coaxial line and the telephone socket are usually separated at both ends of the room, Bridging these two networks is not as simple as wireless technology.
Because wireless home networks are extremely popular, base stations may still need to support wireless home networks. Whether it is a wireless handheld device, an enterprise computer equipped with a wireless local area network interface, and other devices that are still some distance away from a telephone or coaxial line socket, they cannot be supported by HPNA coaxial / telephone lines. Compared with the 802.11 coaxial / wireless solution, if you want to use 802.11 to make up for the deficiencies of HPNA, it will bring a set of inefficient and redundant solutions.
4. Exclusive coaxial transceiver ('HomeCNA')
Many companies also recommend home network solutions based on coaxial cables. They will use a non-standard transmission protocol; in fact, it will be a good technical solution to provide multimedia optimization protocols through coaxial cables Solutions, but they are still less likely to be adopted than solutions based on existing standards, especially extremely popular solutions such as 802.11b / a / g. To develop new exclusive standards and new parts for the cable TV home network, this will be a long and expensive proposal, and the opportunity for multiple manufacturers to participate in this work is very slim; even if this method has many technical advantages, So that it has the ability to become a transmission protocol better than 802.11b / a / g, but they will still be no less than the existing standards that have passed the actual test, especially the existing 802.11 components.
Even in this way, in addition to the coaxial network technology, the set-top box still needs another home network technology to allow devices farther away from the coaxial cable socket to connect; in contrast, the set-top box with a single 802.11 interface Data can be transmitted through wireless communication and coaxial lines, proving that the aforementioned solution is not only inefficient but also expensive.
Dedicated coaxial home network solution can provide 100 Mbps or higher data output, exceeding 54 Mbps that can be achieved by existing 802.11 solutions; it is worth noting that a special working group of 802.11 is studying higher data rates 802.11 extended standards, they will provide greater transmission capacity for high-bandwidth applications and services.
in conclusion
We introduced the concept of hybrid coaxial / wireless home networks, which can use existing 802.11 standards and parts to support high-bandwidth applications and services. Because the data rate is up to 54 Mbps, supports QoS functions, and covers the entire family, the industry has obtained a solution that enables them to provide and distribute various services that require high transmission capacity and QoS steadily in every corner of the home. , Such as video distribution applications.
By adopting the existing 802.11 standard, manufacturers can obtain parts supply from multiple manufacturers, and at the same time ensure that these parts have good interoperability; through the fierce competition and large sales scale of the 802.11 market, it will bring low cost and low risk to the industry solution.
802.11 is very popular with homes and businesses. Many products also use this wireless technology, such as laptops and PDAs with built-in wireless networks and 802.11b security cameras, which will make the application of hybrid coaxial / wireless 802.11 home multimedia networks more widely.
Incremental encoders provide speed, direction and relative position feedback by generating a stream of binary pulses proportional to the rotation of a motor or driven shaft. Lander offers both optical and magnetic incremental encoders in 4 mounting options: shafted with coupling, hollow-shaft, hub-shaft or bearingless. Single channel incremental encoders can measure speed which dual channel or quadrature encoders (AB) can interpret direction based on the phase relationship between the 2 channels. Indexed quadrature encoders (ABZ) are also available for homing location are startup.
Incremental Encoder,6Mm Solid Shaft Encoder,Hollow Rotary Encoder,Elevator Door Encoder
Jilin Lander Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jilinlandermotor.com
