Yu Anqi: Analysis and Suggestions on LED Blue Light Hazard Detection Results
At present, China has become the world's largest producer of LED lamps. However, when the industry shared a feast and the triumphant progress, the medical community expressed concern. Professor Sun Xinghuai, vice president of the Chinese Academy of Ophthalmologists and president of the Shanghai ENT Hospital, said that according to international research results, the blue light emitted by LEDs will cause serious harm or even blindness if it acts on the human eye for a long time. This news has caused widespread concern and frequent comments from netizens on the Internet.
Is the LED light blue really so harmful? Is the so-called "blue light overflow" really a "potential killer" that hurts the eyes? According to the possible blue light hazard of LED products, understand the blue light danger of LED lighting products on the market. The Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Quality Supervision has organized a testing organization to conduct a thorough testing of some LED lighting products.
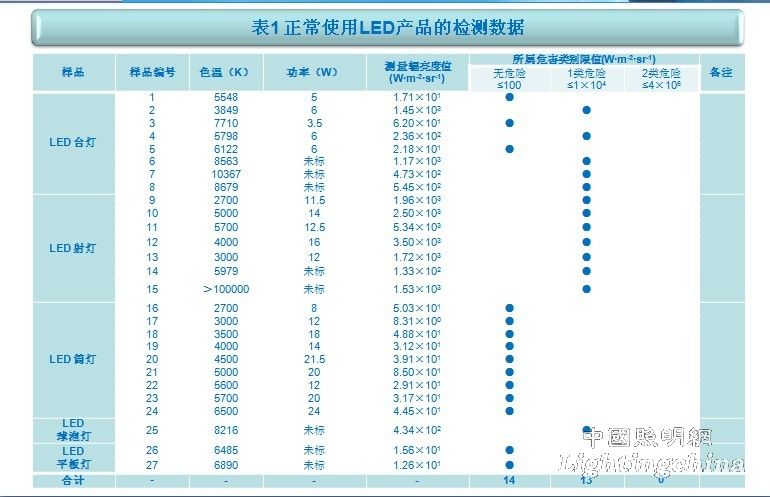
Table I
First, sample source and composition
1. Sample source The total number of samples tested is 27, which are from:
8 samples were purchased from small informal stores;
5 samples were purchased from large supermarkets;
The 14 samples are test samples for large and medium-sized manufacturers.
2. Sample composition
Of the 27 samples, 8 LED desk lamps, 7 LED spotlights, 9 LED downlights, 1 LED bulb and 2 LED panel lights.
Second, the purpose and basis of testing
Purpose: To detect and evaluate the risk of retinal blue light in LED lighting products.
Basis: Detection and classification criteria: GB/T 20145-2006 Photobiosafety of lamps and lamp systems
Judgment document: IECEE CTL (International Electrotechnical Commission - Laboratory Committee) Resolution: DSH 0744
Third, the blue light hazard level and corresponding requirements
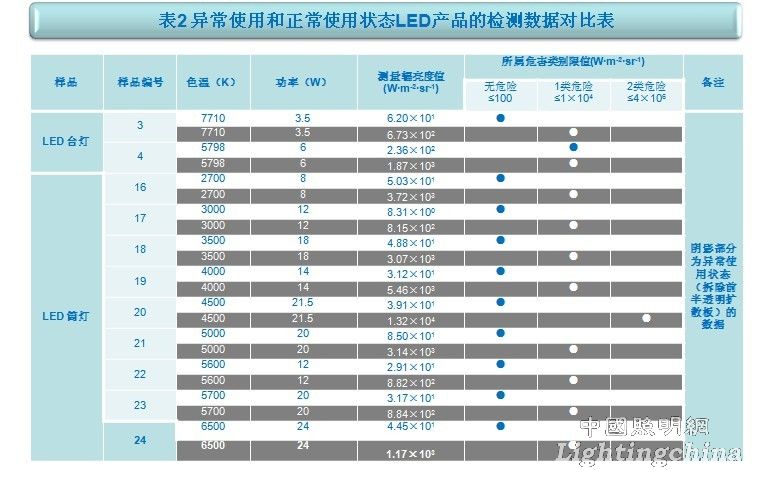
Table II
1. Blu-ray hazard level
According to GB/T 20145-2006 Blu-ray retinal hazard can be classified as:
1) Non-hazardous (radiation ≤ 100 W·m-2·sr-1): The scientific basis of the non-hazard class is that the lamp does not pose any photobiological hazard under the extreme conditions of this standard;
2) Low risk (Class 1) (radiance ≤ 1 × 104 W·m-2·sr-1): the lamp does not pose a hazard under the normal exposure conditions;
3) Danger (Class 2) (radiance ≤ 4 × 106 W · m -2 · sr-1): The light produced by the lamp does not cause the danger of glare and temperature discomfort.
4) High risk (Category 3) (radiance > 4 × 106 W · m - 2 · sr-1): The lamp causes harm in a shorter moment.
2. Corresponding judgment requirements
According to IECEE CTL Resolution DSH 0744:
1) When the brightness is less than 10000 cd/m2 and only visible light is emitted, it is not necessary to classify the hazard level according to GB/T 20145-2006. It can be classified as non-hazardous and can be used directly. If the brightness is greater than 10000 cd/m2, it should be treated as described in 2) or 3) below.
2) If the manufacturer provides a test report indicating that the radiance of the luminaire does not exceed the non-hazardous category and low risk (Class 1) specified in GB/T 20145-2006, the certification body may accept such an LED luminaire and consider it to be normal. There is no photobiological hazard in the case.
3) If the manufacturer does not provide such a claim, it should be tested in accordance with GB/T 20145-2006, and the test results meet the requirements of 2) above.
3. Marking requirements for products of category 2 and above
According to the draft of IEC 62471-2 and IEC 60598-1 8th edition, LED light sources and LED lamps of Class 2 and above have no warning signs and cannot be used directly.
