Smart grid standardization is the premise of grid informationization
Smart grid is the trend of future development. At present, all countries in the world are carrying out technical research in light of their actual conditions, and conducting pilot projects for testing and verification. Realizing the interoperability of devices and systems is one of the main goals of smart grid construction. In order to achieve this goal, a series of standards need to be determined so that multiple technologies can be integrated and information can be integrated. Specifically, the key to promoting the coordinated development of all aspects of the smart grid lies in three aspects: the physical grid, information systems, and business integration. Relying on standards and norms, efforts are made to address issues such as high integration of energy flows, information flows, and business flows. . In the process of smart grid construction, we should adhere to unified planning, unified standards, and unified design principles.
The transition to the smart grid will be long-term. It is neither realistic nor sensible to advocate that all existing equipment and systems be immediately improved or updated. The smart grid supports the gradual transition and the long-term coexistence of multiple technologies. This is because we do not replace simple systems and equipment. Instead, we design the public information model following the core standards of the smart grid and must ensure that the grid is not reduced. Reliability, grid security, and cyber security while avoiding unnecessary expenses. Therefore, the smart grid technology standards have important strategic significance in the smart grid, and will throughout the smart grid construction, determine the success or failure of smart grid construction.
The smart grid core standard is the top priority of the smart grid. The core standards of the smart grid are for grid informationization and interoperability. They have a significant impact on smart grid applications and solutions and are applicable to key standards in the major areas of smart grids. The improvement and improvement of smart grid core standards is the key to the determination of smart grid solutions, and has a significant impact on smart grid solutions and other related standards.
The International Electrotechnical Commission believes that the core standards of the smart grid include: standards for open architecture, interoperability, and network security. The German Standardization Committee believes that the core standards of the smart grid mainly include: standards for open architecture, public information model, monitoring system communication, network security, and market transaction communication.
Through the analysis and comparison of the core standards of smart grids of the world's major countries and international organizations, we believe that China's smart grid standardization safeguards should include the following aspects:
The first is to ensure China’s international leading position in smart grid construction through standardization.
The second is to use smart grid technology standards as a strategic tool to support the social and economic attributes of smart grids through standardization.
The third is to standardize the smart grid as a technical regulation and resolutely implement it.
Fourth, through cooperation with domestic and foreign companies and standard organizations, they have formulated advanced technical standards, promoted the integration and integration of technologies, transformed enterprise standards into national standards, and increased national standards to international standards.
The fifth is to strictly follow the procedures and tools provided by the standard organization for standard formulation, technical testing and verification.
Sixth, in light of the principle of doing something for nothing, we should choose new technologies and new areas to impact international standards. Equivalent adoption should be regarded as a basic strategy for existing international standards, including those being revised or to be revised.
Seventh, according to the progress of the smart grid construction and the maturity of the technology, we must follow the principle of needs and feasibility, grasp the appropriate timing, and issue the standard under the conditions of meeting the maturity of the standard.
It is suggested that in the process of smart grid construction, full attention should be paid to the strategic status of technical standards and the strategic objectives of technical standards should be clearly defined. In the process of formulating the relevant standards, the standard formulation and technical testing and verification are strictly carried out in accordance with the processes and tools provided by the standard organization. Consider the possible impact of core standards enhancements and improvements, eliminate technical barriers, ensure the coordination and consistency of standards, and improve the practicality, operability, and life cycle of standards.
The transition to the smart grid will be long-term. It is neither realistic nor sensible to advocate that all existing equipment and systems be immediately improved or updated. The smart grid supports the gradual transition and the long-term coexistence of multiple technologies. This is because we do not replace simple systems and equipment. Instead, we design the public information model following the core standards of the smart grid and must ensure that the grid is not reduced. Reliability, grid security, and cyber security while avoiding unnecessary expenses. Therefore, the smart grid technology standards have important strategic significance in the smart grid, and will throughout the smart grid construction, determine the success or failure of smart grid construction.
The smart grid core standard is the top priority of the smart grid. The core standards of the smart grid are for grid informationization and interoperability. They have a significant impact on smart grid applications and solutions and are applicable to key standards in the major areas of smart grids. The improvement and improvement of smart grid core standards is the key to the determination of smart grid solutions, and has a significant impact on smart grid solutions and other related standards.
The International Electrotechnical Commission believes that the core standards of the smart grid include: standards for open architecture, interoperability, and network security. The German Standardization Committee believes that the core standards of the smart grid mainly include: standards for open architecture, public information model, monitoring system communication, network security, and market transaction communication.
Through the analysis and comparison of the core standards of smart grids of the world's major countries and international organizations, we believe that China's smart grid standardization safeguards should include the following aspects:
The first is to ensure China’s international leading position in smart grid construction through standardization.
The second is to use smart grid technology standards as a strategic tool to support the social and economic attributes of smart grids through standardization.
The third is to standardize the smart grid as a technical regulation and resolutely implement it.
Fourth, through cooperation with domestic and foreign companies and standard organizations, they have formulated advanced technical standards, promoted the integration and integration of technologies, transformed enterprise standards into national standards, and increased national standards to international standards.
The fifth is to strictly follow the procedures and tools provided by the standard organization for standard formulation, technical testing and verification.
Sixth, in light of the principle of doing something for nothing, we should choose new technologies and new areas to impact international standards. Equivalent adoption should be regarded as a basic strategy for existing international standards, including those being revised or to be revised.
Seventh, according to the progress of the smart grid construction and the maturity of the technology, we must follow the principle of needs and feasibility, grasp the appropriate timing, and issue the standard under the conditions of meeting the maturity of the standard.
It is suggested that in the process of smart grid construction, full attention should be paid to the strategic status of technical standards and the strategic objectives of technical standards should be clearly defined. In the process of formulating the relevant standards, the standard formulation and technical testing and verification are strictly carried out in accordance with the processes and tools provided by the standard organization. Consider the possible impact of core standards enhancements and improvements, eliminate technical barriers, ensure the coordination and consistency of standards, and improve the practicality, operability, and life cycle of standards.
The sensor includes linear encoder and rotary encoder, which is used for the position measurement of speed, displacement and angle. Yuheng optics can provide rotary encoders based on optical, magnetic and gear principles, linear encoders based on optical principles and supporting products.
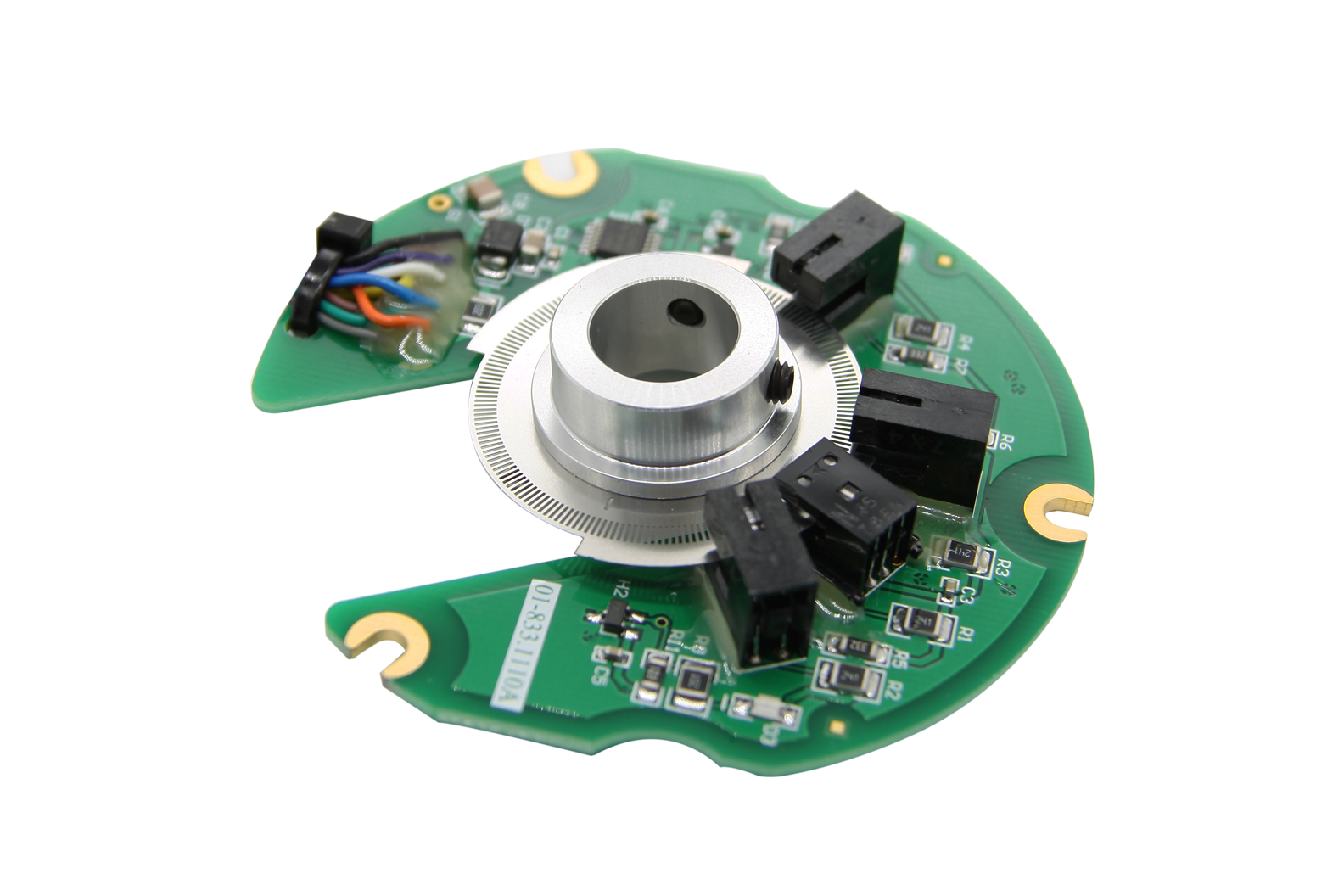
Custom Sensor,Clintegrity Encoder,Absolute Angle Encoder,Small Rotary Encoders
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yhenoptics.com
